For a diatomic gas change in internal energy for unit change in temperature for constant pressure and constant volume is U1 and U2 respectively. U1 : U2 is
Important Questions on Thermodynamics
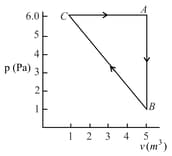
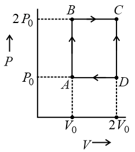
For the given cyclic process as shown for a gas, the work done is:
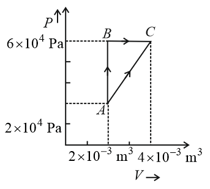
In process AB, of heat is added to the system and in process BC, of heat is added to the system. The heat absorbed by the system in the process AC will be:
The initial pressure and volume of a given mass of an ideal gas with , taken in a cylinder fitted with a piston, are and respectively. At this stage the gas has the same temperature as that of the surrounding medium which is It is adiabatically compressed to a volume equal to
Subsequently the gas is allowed to come to thermal equilibrium with the surroundings. What is the heat released to the surrounding?
The corresponding P - V diagram for the process is (all figures are schematic and not drawn to scale) :
(Take , where is gas constant)
In the given diagram, a monoatomic gas is first compressed adiabatically from state state . Then it expands isothermally from state to state . [Given : ].
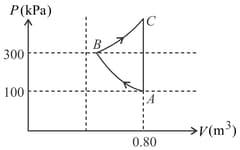
Which of the following statement(s) is(are) correct?
An ideal gas of density enters a chimney of height at the rate of from its lower end, and escapes through the upper end as shown in the figure. The cross-sectional area of the lower end is and the upper end is . The pressure and the temperature of the gas at the lower end are and , respectively, while its temperature at the upper end is . The chimney is heat insulated so that the gas undergoes adiabatic expansion. Take and the ratio of specific heats of the gas . Ignore atmospheric pressure.
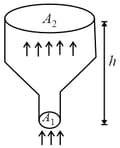
Which of the following statement(s) is(are) correct?
[ is the gas constant]
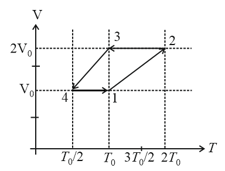
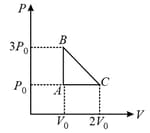
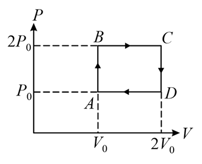
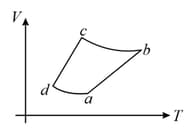
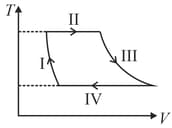
The above diagram represents the thermodynamic cycle of an engine, operating with an ideal mono-atomic gas. The amount of heat, extracted from the source in a single cycle, is:
Two moles of an ideal monoatomic gas occupies a volume at . The gas expands adiabatically to a volume . Calculate the final temperature of the gas and change in its internal energy.
(Given is gas constant)