EASY
Earn 100
For magnification in spherical mirrors, the object height is taken:
(a)negative.
(b)positive.
(c)positive for real images.
(d)negative for virtual images.
50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Light
EASY
EASY
( principal focus, centre of curvature, pole)
EASY
EASY
EASY
EASY
EASY
 in convex mirror looks like
in convex mirror looks likeEASY
EASY
MEDIUM
Focal length of one convex mirror is and object distance is , then find the image distance.
EASY
EASY
EASY
EASY
HARD
A concave mirror of focal length 15cm forms an image. The position of the object when the image is virtual and linear magnification is 2 is.
EASY
In the following diagram ‘’ is a mirror and ‘’ is an object and ‘’ is the magnified image of ‘’ formed by the mirror. The mirror ‘’ is a:
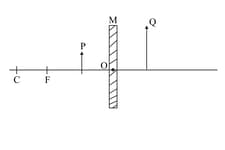
EASY
EASY
Which effect is responsible for blue colour of smoke?
EASY
If a mirror forms erect image for objects placed between pole and focus, and it forms real-inverted image for object placed anywhere between focus and infinity, then the mirror is:
EASY

