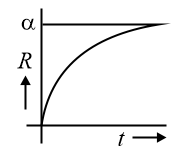
For nuclei with ,

Important Points to Remember in Chapter -1 - The Nucleus from H C Verma CONCEPTS OF PHYSICS [VOLUME 2] Solutions
1. Atomic Nucleus:
The average radius of the nucleus may be written as
,
is mass number.
2. Mass Defect and Binding Energy:
The binding energy of nucleus of mass , is given by
3. Nuclear Reactions:
(i) Alpha - decay process:
-value
(ii) Beta- minus decay:
-value
(iii) Beta plus decay:
-value
(iv) When the atomic electron is captured, -rays are emitted.
-value
4. Nuclear Fission:
Discovered by Hahn and Strassmann in By attack of a particle on a heavy nucleus and splitting it into two or more lighter nuclei, a certain mass disappears which is obtained in the form of energy.
5. Nuclear Fusion:
It is the phenomenon of fusing two or more lighter nuclei to form a single heavy nucleus.
The product is more stable than the reactants .
mass defect,
Energy released is
The total binding energy and binding energy per nucleon of , both are more than of and
6. Radioactive Decay Law:
(i) In radioactive decay, the number of nuclei at instant is given by , - decay constant.
(ii) Activity of sample:
(iii) Activity per unit mass is called specific activity.
(iv) Half-life:
(v) Average life:
(vi) A radioactive nucleus can decay by two different processes having half-lives and respectively. Effective half-life of the nucleus is given by .
(vii) Probability of a nucleus for survival of time
7. Parallel radioactive disintegration:
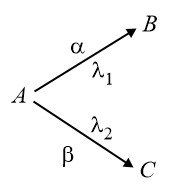
Let the initial number of nuclei of is then at any time number of nuclei of are given by
A disintegrates into and by emitting particle.
Now,
8. Radioactive Disintegration with Successive Production:
is being produced at a rate .
disintegrates into .
when is maximum
By equation Number of nuclei is