Four different lengths of DNA, A to D, were cut with the restriction enzyme EcoRI. These fragments had the following numbers of restriction sites for this enzyme: A- 5, B- 7, C- 0, and D- 3. State the number of fragments that will be formed from each length of DNA after incubation with EcoRI.

Important Questions on Genetic Technology
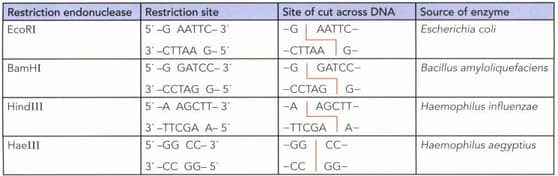
Describe the features of the restriction sites shown in the table below.
Rearrange the statements below to produce a flow diagram showing the steps involved in producing bacteria capable of synthesising a recombinant human protein, such as insulin or factor VIII.
A. Insert the plasmid into a host bacterium.
B. Isolate mRNA for the gene required.
C. Use ligase to seal the sugar-phosphate backbone of the recombinant plasmid.
D. Use DNA polymerase to produce double-stranded eDNA.
E. Clone the modified bacteria and harvest the recombinant protein.
F. Use reverse transcriptase to produce single-stranded cDNA.
G. Use a restriction enzyme to cut plasmids.
H. Use an enzyme to add a short length of single-stranded DNA to form sticky ends.
I. Form recombinant plasmids by complementary base pairing.
J. Mix the double-stranded DNA with plasmids.