Four infinitely long parallel wires pass through the four corners of a square of side that lies in a plane perpendicular to the wires (see figure).
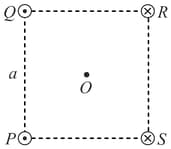
They all carry equal steady currents . Currents in the wires passing through and point out of the page, and the currents in the wires passing through and point into the page as shown in the figure. The magnitude of the magnetic field at the centre of the square is

Important Questions on Moving Charges and Magnetism
The graph showing the variation of the magnetic field strength (B) with distance (r) from a long current carrying conductor is
A long straight wire of circular cross-section (radius ) is carrying steady current The current is uniformly distributed across this cross-section. The magnetic field is
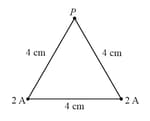
Two long straight wires vertically pierced the plane of the paper at vertices of an equilateral triangle as shown in figure. They each carry out of the paper. The magnetic field at the third vertex has magnitude.
Two long straight parallel wires, carrying (adjustable) currents and , are kept at a distance apart. If the force between the two wires is taken as 'positive' when the wires repel each other and 'negative' when the wires attract each other, the graph showing the dependence of , on the product , would be:
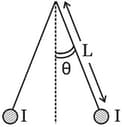
Two long currents carrying thin wires, both with current , are held by insulating threads of length L and are in equilibrium as shown in the figure, with threads making an angle ' ' with the vertical. If wires have a mass per unit length then the value of is:
( gravitational acceleration)
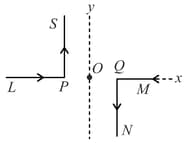
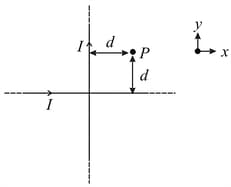
As shown in the figure, two infinitely long, identical wires are bent by and placed in such a way that the segments and are along the - axis, while segments and are parallel to the - axis. If and the magnitude of the magnetic field at is and the two wires carry equal currents (see figure), the magnitude of the current in each wire and the direction of the magnetic field at will be
A wire carrying current has the shape as shown in adjoining figure. Linear parts of the wire are very long and parallel to -axis while semicircular portion of radius is lying in - plane. Magnetic field at point is :
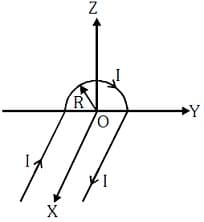
Two very long, straight, and insulated wires are kept at angle from each other in plane as shown in the figure.
These wires carry currents of equal magnitude , whose direction are shown in the figure. The net magnetic field at point will be:

