EASY
Earn 100
Give two examples of hypogeal germination.
Important Questions on The Plant: Structure and Function
EASY
Choose the answer from the bracket.
The fruit and seed shown below are dispersed by _____. (wind/water/animals/birds).
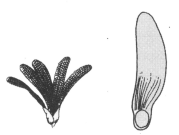
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY
The seeds of _____ are pollinated by wind.
(Choose from cotton, water lily, mango, tomato).
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY
EASY
EASY
EASY
HARD
Fill in the blank with the right word.
(carrot, hook, coconut, Ruellia tuberose)
The fruits of _____ explode when they come in contact with water.
EASY
Choose the right word and fill in the blank provided below.
The process by which seeds are scattered away from the mother plant is called _____ (germination /dispersal).
MEDIUM
Fill in the blank with the most appropriate word:
Some seeds such as those of Indian elm have wings that help in _____ by air. (dispersal/pollination)
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY

