EASY
Earn 100
Go through the following diagram describing muscle contraction. Identify the parts from A to D.
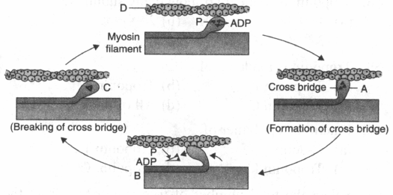

(a)A: Sliding/Rotation, B: Actin filament, C: Myosin head, D: ATP.
(b)A: Myosin head, B: Sliding/Rotation, C: ATP, D: Actin filament.
(c)A: Sliding/Rotation, B: Myosin head, C: Actin filament, D: ATP.
(d)A: Actin filament, B: Sliding/Rotation, C: ATP, D: Myosin head.
50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Locomotion and Movement
MEDIUM
HARD
During muscular contraction which of the following events occur?
(a) 'H' zone disappears
(b) 'A' band widens
(c) 'I' band reduces in width
(d) Myosin hydrolyzes ATP, releasing the ADP and Pi
(e) Z-lines attached to actins are pulled inwards.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
EASY
HARD
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
(i) Muscles show three essential properties such as excitability, conductivity and contractility.
(ii) Muscular tissue is endodermal in origin except muscle of iris and ciliary body.
(iii) The cytoplasm of muscle fibre has several myofibrils.
(iv) Skeletal muscles exhibit slow and prolonged contractions.
(v) The regular arrangement of myosin and actin filaments is responsible for alternate dark and light bands of striated muscle.
MEDIUM
EASY
-line
-line
-zone
-band
EASY
EASY
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
HARD
MEDIUM

