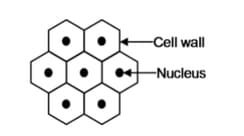
How are companion cells helpful to sieve tubes?
Important Questions on Plant Water Relation
A. Made up of dead cells
B. Have very little intercellular space
C. Cells are irregularly thickened at the corners
D. Cell wall contains lignin
Observe the given diagram and read the following statements.
(i) These are cells of collenchyma tissue.
(ii) At maturity these cells lose their nucleus and cytoplasm.
(iii) The cells are living and thick at their corners.
(iv) This tissue gives flexibility to plant parts.
Correct statements are:
Incoming sugars are actively transported out and removed as complex carbohydrates.
Increase of water potential.
Increase of hydrostatic pressure in sieve tubes.
Transport of water into sieve tubes by osmosis.
The combination of numbered terms that correctly completes all the following statements is
i. Transport through the phloem is __1__ while transport through the xylem is __2__.
ii. Loading of sugars into the phloem is __3__ at the source.
iii. Movement of water out of the phloem at the sink is __4__.
A) Loading of sugars into phloem setup a water potential gradient that facilitates mass movement in phloem.
B) Sucrose moves into companion cell and then to phloem sieve tube cell by active transport.
C) A hypertonic condition in phloem facilitating water from the xylem into phloem by osmosis.
D) All sink sugars are transported out of the phloem producing high water potential with returning of water to xylem.
E) With increase in hydrostatic pressure in phloem pressure flow begin and sap moves through phloem.
Which of the following is not a component of phloem?
In "Pressure Flow" hypothesis, sugars are transported from 'source' to 'sink'. The initial steps which occur during this physiological process are shown here.
I. In leaves glucose is converted to sucrose.
II. Sucrose moves from sieve tube cells to companion cells by active transport.
III. Loading of sucrose produces a hypotonic condition in the phloem.
IV. Water in the adjacent xylem moves into phloem by osmosis.
Identify the above correct statements: