How do roots of monocot plants differ from that of dicot plants?
In having conjunctive tissue between xylem and phloem
In having protoxylem situated towards the periphery
In having a well-developed pith
Important Questions on Anatomy of Flowering Plants
Read the following statements about the vascular bundles:
(a) In roots, xylem and phloem in a vascular bundle are arranged in an alternate manner along the different radii.
(b) Conjoint closed vascular bundles do not possess cambium.
(c) In open vascular bundles, cambium is present in between xylem and phloem.
(d) The vascular bundles of dicotyledonous stem possess endarch protoxylem.
(e) In monocotyledonous root, usually there are more than six xylem bundles present.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
A) Epidermal cells are parenchymatous and have small amount of cytoplasm
B) Gymnosperms have vessels in their xylem
C) In bicollateral vascular bundle, phloem is present on either side of cortex
D) Root endodermal cells have deposition of water impermeable, suberin as casparian strips
Represent the union of two sets by Venn diagram for each of the following.
is a prime number between and
is an odd number between and
A transverse section of a typical monocot root shows
(a) Barrel-shaped endodermal cells with casparian strips.
(b) Diarch to hexarch vascular bundles.
(c) Protoxylem towards center
and metaxylem towards periphery.
(d) Large well-developed parenchymatous pith in center.
Mark A, B, C, and D in the given figure.
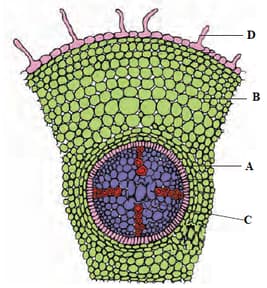
Two cross-sections of stem and root appear simple when viewed by the naked eye. But under a microscope, they can be differentiated by:

