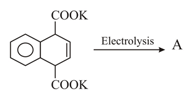
MEDIUM
Earn 100
How many moles of Grignard reagent will consume when it reacts with following the compound?
100% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
HARD
With dehydrating agent present which dicarboxylic acid is least reactive towards forming an anhydride?
MEDIUM
The major product obtained in the reaction of aniline with acetic anhydride is
MEDIUM
The major product of the following reaction is:
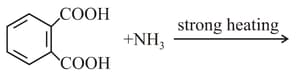
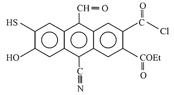
MEDIUM
The decreasing order of ease of alkaline hydrolysis for the following esters is
EASY
In the presence of a small amount of phosphorous, aliphatic carboxylic acid reacts with chlorine or bromine to yield a reaction in which, hydrogen is been replaced by halogen. This reaction is known as
MEDIUM
chlorosodium acetate on boiling with aqueous sodium nitrite gives
HARD
In the reaction,
,
the product C is :
MEDIUM
Which of the following derivatives of alcohols is unstable in an aqueous base?
MEDIUM
The major product formed in the following reaction is
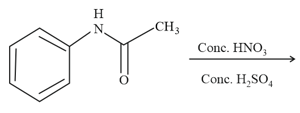
HARD
The most suitable reagent for the given conversion is:
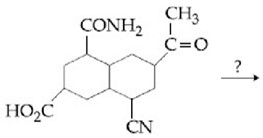
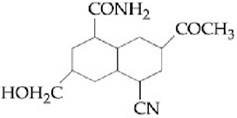
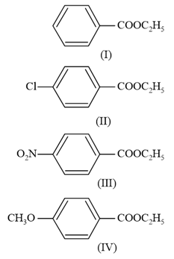
MEDIUM
Which one of the following esters gets hydrolyzed most easily under alkaline conditions?
HARD
List includes starting materials and reagents of selected chemical reactions. Listgives structures of compounds that may be formed as intermediate products and/or final products from the reactions of List.
| List-I | List-II |
|---|---|
(I) 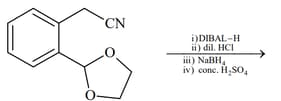 |
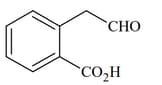 |
(II) 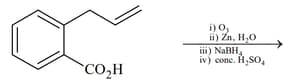 |
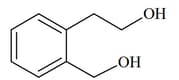 |
(III) 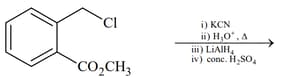 |
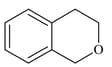 |
(IV) 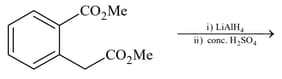 |
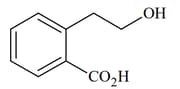 |
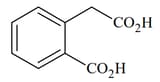 |
|
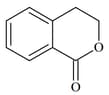 |
Which of the following options has the correct combination considering List and List?
HARD
The major product of the following reaction is:
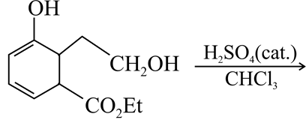
MEDIUM
Propanoic acid undergoes reaction to give chloropropanoic acid. The product obtained is
MEDIUM
Hydrolysis of aromatic amide gives
MEDIUM
Which of the following acid will form an (a) Anhydride on heating and (b) Acid imide on strong heating with ammonia?
EASY
Ethyl acetate reacts with to form
MEDIUM
An organic compound A upon reacting with gives B. On heating, B gives C. C in presence of KOH reacts with Br2 to give CH3CH2NH2. A is :
EASY
The correct structure of the product in the following reaction is