Hydrogen gas, , reacts with iodine gas, , to form hydrogen iodide, :
The mechanism of the two-step reaction is considered to be:
step : fast
step : slow
What is the rate equation for the overall reaction?
rate
rate
rate
Important Questions on Chemical Kinetics
For an elementary chemical reaction, , the expression for is:
In the following reaction;
‘A’ and ‘B’ respectively can be:
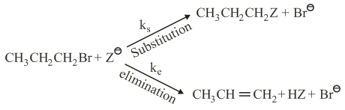
where,
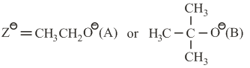
and , are respectively, the rate constants for substitution and elimination, and , the correct option is ________
Consider the following reactions
The order of the above reactions are respectively. The following graph is obtained when log[rate] vs.log[conc.] are plotted:
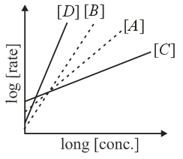
Among the following, the correct sequence for the order of the reactions is :
Rate
If the concentration of A is kept the same but that of B is doubled what will happen to the rate itself?
The results given in the below table were obtained during kinetic studies of the following reaction:
| Experiment | Initial rate/ | ||
| I | |||
| II | |||
| III | |||
| IV | X | ||
| V | Y |
X and Y in the given table are respectively :
If the concentration of is increased from , keeping the value of at , the rate constant will be:
...(i)
...(ii)
The closest rate constant for the overall reaction
is:
Which of the following expression is correct for the rate of reaction given below ?
The initial concentration of is and it is after 30 minutes. The rate of formation of is:
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
The overall order of the reaction will be

