EASY
Earn 100
Identify a concentration verses time graph for a second order reaction with single reactant.
(a)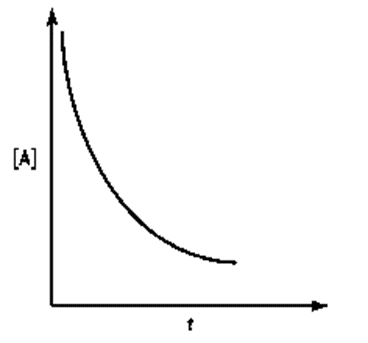

(b)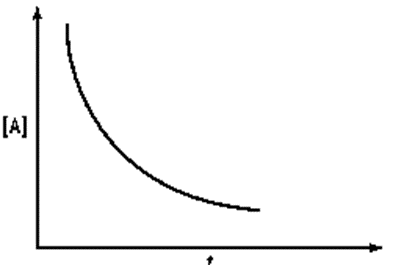

(c) 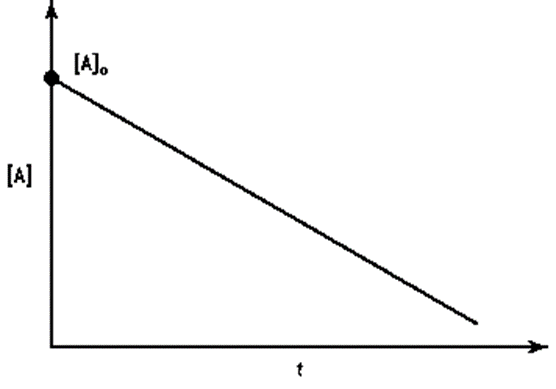
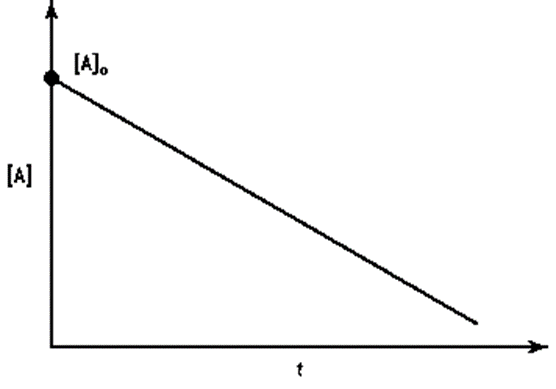
(d)None of the above
50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Chemical Kinetics (AHL)
MEDIUM
For a reaction, consider the plot of versus given in the figure. If the rate constant of this reaction at is , then the rate constant at is:
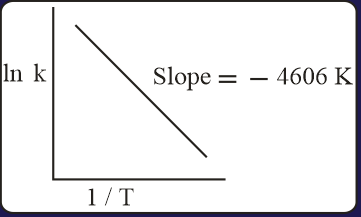
EASY
HARD
For an elementary chemical reaction, , the expression for is:
EASY
HARD
HARD
The activation energy of the backward reaction exceeds that of the forward reaction by (in ). If the pre-exponential factor of the forward reaction is times that of the reverse reaction, the absolute value of for the reaction at is ____.
(Given; and is the Gibbs energy)
MEDIUM
Which one of the following statements is correct?
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY
For the reaction,
and
when,
If, then the integrated rate law will he
HARD
HARD
(Assume that all these gases behave as ideal gases)
EASY
Rate
If the concentration of A is kept the same but that of B is doubled what will happen to the rate itself?
MEDIUM
[Gas constant, ]
MEDIUM
| Initial Concentration (A) | Initial Concentration (B) | Initial rate of formation of C |
|---|---|---|
The rate law for the formation of is
HARD
Consider the given plots for a reaction obeying Arrhenius equation (and are rate constant and activation energy, respectively )
(I)
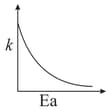
(II)
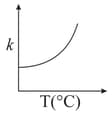
MEDIUM
EASY

