EASY
Earn 100
In Searle's apparatus we have two wires. During experiment, we study the extension in one wire. The use of second wire is -
(a)to support the apparatus because it is heavy and may not break single wire.
(b)to compensate the changes in length caused by changes in temperature of atmosphere during experimentation.
(c)to keep the apparatus in level so that extension is measured accurately.
(d)all the three above.
50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Elasticity
HARD
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
HARD
HARD
EASY
MEDIUM
= Young's modulus of the material of rod, coefficient of linear expansion
EASY
MEDIUM
HARD
EASY
HARD
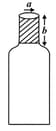
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
HARD
(gravitational acceleration)

