In a microscope of the type shown in the figure, the focal length of the objective is and that of the eyepiece is The distance between the lenses is (a) What is the tube length ? (b) If image in the figure is to be just inside focal point , how far from the objective should the object be? What then are the lateral magnification of the objective.
(d) the angular magnification of the eyepiece, and (e) the overall magnification of the microscope?
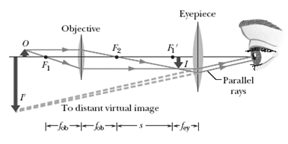
(d) the angular magnification of the eyepiece, and (e) the overall magnification of the microscope?


Important Questions on Images
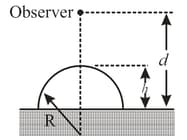
In the figure, and index of refraction A paperweight is constructed by slicing through the sphere along a plane that is from the center of the sphere, leaving height The paperweight is placed on a table and viewed from directly above by an observer who is distance from the tabletop (Figure). When viewed through the paperweight, how far away does the tabletop appear to be to the observer?
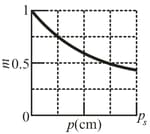
The figure gives the lateral magnification of an object versus the object distance from a lens, as the object is moved along the central axis of the lens through a range of values for out to What is the magnification of the object when the object is from the lens?
Object stands on the central axis of a thin symmetric lens. For this situation, each problem in table refers to the lens type, converging or diverging the focal distance the object distance the image distance and the lateral magnification (All distances are in ) It also refers to whether the image is real or virtual inverted or non-inverted from and on the same side of the lens as or on the opposite side. Fill in the missing information, including the value of when only inequality is given. Where only a sign is missing, answer with the sign.
The figure gives the lateral magnification of an object versus the object distance from a spherical mirror, as the object is moved along the mirror's central axis through a range of values for . The horizontal scale is set by . What is the magnification of the object when the object is from the mirror?
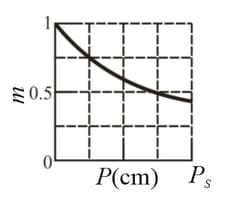
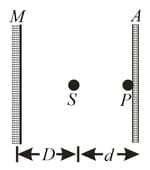
In the figure, an isotropic point source of tight is positioned at distance from a viewing screen and the light intensity at point (level with ) is measured. Then a plane mirror is placed behind at distance . By how much is multiplied by the presence of the mirror, if ?
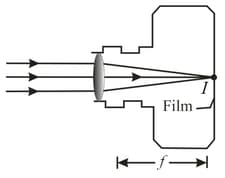
The figure a shows the basic structure of an old film camera. A lens can be moved forward or back to produce an image on film at the back of the camera. For a certain camera, with the distance between the lens and the film set at parallel light rays from a very distant object converge to a point image on the film, as shown. The object is now brought closer, to a distance of and the lens-film distance is adjusted so that an inverted real image forms on the film figure . What is the lens-film distance now? (b) By how much was distance changed?
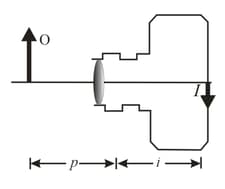
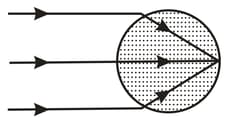
In the figure, a beam of parallel light rays from a laser is incident on a solid transparent sphere of index of refraction . (a) If a point image is produced at the back of the sphere, what is the index of refraction of the sphere? (b) What index of refraction, if any, will produce a point image at the center of the sphere?