In a neutral conducting hollow sphere of inner and outer radii and respectively, a point charge is placed at point , that is from the centre of the hollow sphere. An external uniform electric field of magnitude is also applied. Net electric force on this charge is , away from the centre of the sphere as shown. Then find:
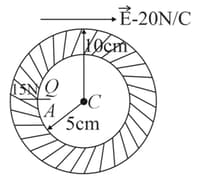
(a) Force due to external electric field on the outer surface of the shell.
(b) Net force on the shell.
(c) Net force on a point charge due to the shell.


Important Questions on Electrostatics
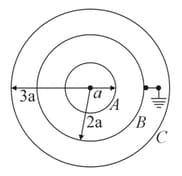
The figure shows a system of three concentric metal shells and with radii and respectively. Shell is earthed and shell is given a charge . Now if shell is connected to shell , then find the final charge on the shell .
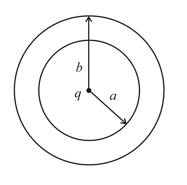
A point charge is brought from infinity (slowly so that heat developed in the shell is negligible) and is placed at the centre of a conducting neutral spherical shell of inner radius and outer radius , then find work done by external agent.
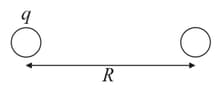
Consider two solid dielectric spheres of radius , separated by a distance . One of the spheres has a charge , and the other is neutral (see figure.) We double the distance between two spheres. How much charge should reside on the first sphere now so that the force between the spheres remains the same ?
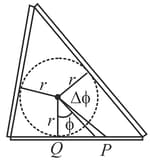
A triangle is made from thin insulating rods of different lengths, and the rods are uniformly charged, i.e., the linear charge density on each rod is uniform and the same for all three rods. Find a particular point in the plane of the triangle at which the electric field strength is zero.
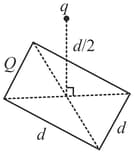
A square of side , made from a thin insulating plate, is uniformly charged and carries a total charge of . A point charge is placed on the symmetrical normal axis of the square at a distance from the plate. How large is the force acting on the point charge?
A very long straight thread is oriented at right angles to an infinite conducting plane; its end is separated from the plane by a distance . The thread carries a uniform charge of linear density . Suppose the point is the trace of the thread on the plane. Find the surface density of the induced charge on the plane
(a) At the point (b) As a function of a distance from the point .
