In elastic collision, energy transfer takes place when
Important Questions on Laws of Motion
A sphere of mass moving with velocity collides head-on another sphere of same mass which is at rest. The ratio of final velocity of the second sphere to the initial velocity of the first sphere is ( is the coefficient of restitution and collision is inelastic)
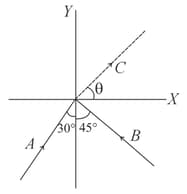
This question has and of the four choices given after the Statements, choose the one that best describes the two Statements.
A point particle of mass moving with speed collides with stationary point particle of mass . If the maximum energy loss possible is given as
then .
Maximum energy loss occurs when the particles get stuck together as a result of the collision.
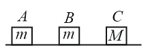
A block of mass rests on a horizontal table. The coefficient of friction between the block and the table is . When hit by a bullet of mass moving with speed , that gets embedded in it, the block moves and comes to stop after moving a distance of on the table. If a freely falling object were to acquire speed after being dropped from height , then neglecting energy losses and taking , the value of is close to
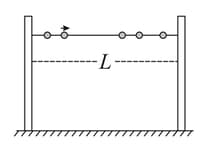
A large number of identical beads, each of mass and radius are strung on a thin smooth rigid horizontal rod of length and are at rest at random positions. The rod is mounted between two rigid supports (see figure). If one of the beads is now given a speed , the average force experienced by each support after a long time is (assume all collisions are elastic):