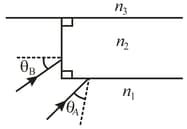
In figure, light from ray refracts from material into a thin layer of material crosses that layer and is then, incident at the critical angle on the interface between materials and What is the value of incident angle If is decreased, does part of the light refract into material Light from ray refracts from material into the thin layer, crosses that layer and is then, incident at the critical angle on the interface between materials and . What is the value of incident angle If is decreased, does part of the light refract into material


Important Questions on Electromagnetic Waves
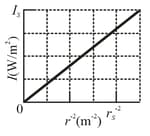
The intensity of light from an isotropic point source is determined as a function of distance from the source. Figure gives the intensity versus the inverse square of that distance. The vertical axis scale is set by and the horizontal axis scale is set by . What is the power of the source?
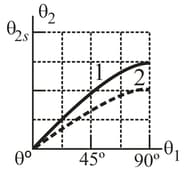
In the figure, a light ray in water is incident at angle on a boundary with an underlying material, into which some of the light refracts. There are two choices of underlying material. For each, the angle of refraction versus the incident angle is given in the figure . The vertical axis scale is set by . Without calculation, determine whether the index of refraction of material and material is greater or less than the index of water What is the index of refraction of material and material ?
A certain helium-neon laser emits red light in a narrow band of wavelengths centered at and with a "wavelength width" (such as on the scale of figure of ) What is the corresponding "frequency width" for the emission?
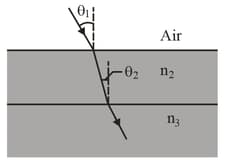
In the figure, a light ray in air is incident on a flat layer of material that has an index of refraction, . Beneath material , is material with an index of refraction . The ray is incident on the air-material interface at the Brewster angle for that interface. The ray of light refracted into material happens to be incident on the material -material interface at the Brewster angle for that interface. What is the value of ?
For comparison, find the ratio of to the Earth's sea-level atmospheric pressure, which is
