HARD
Upper Secondary: IGCSE
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
In humans, the allele for red hair, b is recessive to the allele for brown hair, B. A man and his wife both have brown hair. They have five children, three of whom have red hair, while two have brown hair. Explain how this may happen, using a genetic diagram to explain the answer.

Important Questions on Inheritance
HARD
Upper Secondary: IGCSE
IMPORTANT
HARD
Upper Secondary: IGCSE
IMPORTANT
HARD
Upper Secondary: IGCSE
IMPORTANT
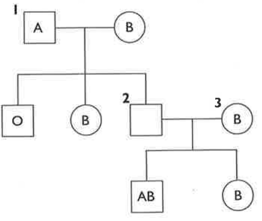
The pedigree diagram shows the known blood group in three generations of a family. Squares represent male and circle represent the females. What are the genotypes of 1 and 3? What is the blood group of 2?
HARD
Upper Secondary: IGCSE
IMPORTANT
HARD
Upper Secondary: IGCSE
IMPORTANT
HARD
Upper Secondary: IGCSE
IMPORTANT
Explain the difference between gene and allele.
HARD
Upper Secondary: IGCSE
IMPORTANT
Explain the difference between dominant and recessive trait.
HARD
Upper Secondary: IGCSE
IMPORTANT
Explain the difference between homozygous and heterozygous.
