EASY
NEET
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
In some chordates, the notochord is modified as the vertebral column. Such animals are called vertebrates. Which one of the following statements makes sense?
(a)All chordates are vertebrates, but all vertebrates are not chordates
(b)All vertebrates are chordates and all chordates are vertebrates
(c)All vertebrates are chordates but all chordates are not vertebrates
(d)Chordates are not vertebrates and vertebrates are not chordates
100% studentsanswered this correctly

Important Questions on Animal Kingdom
EASY
NEET
IMPORTANT
A common characteristic of all vertebrates without exception is
MEDIUM
NEET
IMPORTANT
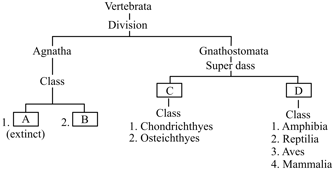
Go through the following flow chart for the division of subphylum Vertebrata. Fill in the gaps A, B, C, and D and select the correct option.
EASY
NEET
IMPORTANT
Match column I with II and select the correct option from the given codes.
| I | II | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | Wings | (i) | Reptiles |
| (b) | Operculum | (ii) | Chondrichthyes |
| (c) | Scutes | (iii) | Birds |
| (d) | Cartilaginous endoskeleton | (iv) | Osteichthyes |
MEDIUM
NEET
IMPORTANT
Match the excretory organs listed under column I with the animals given under column II and select the correct option.
I (Excretory organs) |
II (Animals) |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | Nephridia | (i) | Hydra |
| (b) | Malpighian tubules | (ii) | Leech |
| (c) | Protonephridia | (iii) | Shark |
| (d) | Kidneys | (iv) | Roundworms |
| (v) | Cockroach |
MEDIUM
NEET
IMPORTANT
To which classes do the following animals belong?
A — Petromyzon, B — Scoliodon, C — Pristis
EASY
NEET
IMPORTANT
Which of the following is/are not the characteristics of the Class Osteichthyes?
(i) Body is streamlined and mouth is terminal.
(ii) Gills are covered by operculum.
(iii) Skin covered with cycloid and placoid scales.
(iv) Many of them are viviparous.
EASY
NEET
IMPORTANT
Select the correct option in respect of characteristics of each group.
| Cyclostomes | Chondrichthyes | Osteichthyes | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (i) | Sucking mouth | Ventral mouth | Terminal mouth |
| (ii) | Scales absent | Placoid scales | Cycloid/Ctenoid scales |
| (iii) | Marine | Marine | Marine and freshwater |
| (iv) | pairs of gills |
pairs of gills without operculum |
pairs of gills with operculum |
EASY
NEET
IMPORTANT
Match column I with II and select the correct option from the given codes.
| I | II | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | Cartilaginous fishes | (i) | Usually external fertilisation |
| (b) | Bony fishes | (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) |
Internal fertilization Mostly oviparous Mostly viviparous Direct development |
