HARD
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
In the arrangement shown in figure the masses of the bar and of the wedge, as well as the wedge angle , are known. The masses of the pulley and the thread are negligible. The friction is absent. Find the acceleration of the wedge .
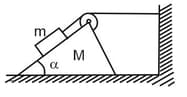

Important Questions on PHYSICAL FUNDAMENTALS OF MECHANICS
HARD
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
Problems in General Physics>Chapter 1 - PHYSICAL FUNDAMENTALS OF MECHANICS>THE FUNDAMENTAL EQUATION OF DYNAMICS>Q 1.86.
A ball suspended by a thread swings in a vertical plane so that its acceleration values in the extreme and the lowest position are equal. Find the thread deflection angle in the extreme position.HARD
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
Problems in General Physics>Chapter 1 - PHYSICAL FUNDAMENTALS OF MECHANICS>THE FUNDAMENTAL EQUATION OF DYNAMICS>Q 1.101.
Having gone through a plank of thickness , a bullet changed its velocity from to . Find the time of motion of the bullet in the plank, assuming the resistance force to be proportional to the square of the velocity.HARD
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
Problems in General Physics>Chapter 1 - PHYSICAL FUNDAMENTALS OF MECHANICS>LAWS OF CONSERVATION OF ENERGY, MOMENTUM, AND ANGULAR MOMENTUM>Q 1.118.
A particle has shifted along some trajectory in the plane from point whose radius vector to point with the radius vector . During that time the particle experienced the action of certain forces, one of which being . Find the work performed by the force . (Here and are given in SI units.)HARD
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
Problems in General Physics>Chapter 1 - PHYSICAL FUNDAMENTALS OF MECHANICS>LAWS OF CONSERVATION OF ENERGY, MOMENTUM, AND ANGULAR MOMENTUM>Q 1.119.
A locomotive of mass starts moving so that its velocity varies according to the law , where is a constant, and is the distance covered. Find the total work performed by all the forces which are acting on the locomotive during the first seconds after the beginning of motion.HARD
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
Problems in General Physics>Chapter 1 - PHYSICAL FUNDAMENTALS OF MECHANICS>LAWS OF CONSERVATION OF ENERGY, MOMENTUM, AND ANGULAR MOMENTUM>Q 1.158.
A steel ball of mass falls from the height on the horizontal surface of a massive slab. Find the cumulative momentum that the ball imparts to the slab after numerous bounces, if every impact decreases the velocity of the ball times.HARD
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
Problems in General Physics>Chapter 1 - PHYSICAL FUNDAMENTALS OF MECHANICS>LAWS OF CONSERVATION OF ENERGY, MOMENTUM, AND ANGULAR MOMENTUM>Q 1.169.
Particle experiences a perfectly elastic collision with a stationary particle . Determine their mass ratio, if
after a head-on collision the particles fly apart in the opposite directions with equal velocities,
the particles fly apart symmetrically relative to the initial motion direction of particle 1 with the angle of divergence .
HARD
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
Problems in General Physics>Chapter 1 - PHYSICAL FUNDAMENTALS OF MECHANICS>LAWS OF CONSERVATION OF ENERGY, MOMENTUM, AND ANGULAR MOMENTUM>Q 1.170.
A ball moving translationally collides elastically with another, stationary, ball of the same mass. At the moment of impact, the angle between the straight line passing through the centre of the balls and the direction of the initial motion of the striking ball is equal to . Assuming the balls to be smooth, find the fraction of the kinetic energy of the striking ball that turned into potential energy at the moment of the maximum deformation.HARD
JEE Main
IMPORTANT
Problems in General Physics>Chapter 1 - PHYSICAL FUNDAMENTALS OF MECHANICS>UNIVERSAL GRAVITATION>Q 1.220.
At what height over the Earth's pole, the free-fall acceleration decreases by (1) one per cent (2) by half?