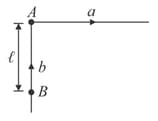
In the figure shown, and are two particles which start from rest. has constant acceleration in the direction shown. also increases its speed at a constant rate but the direction of velocity is always towards . Find the time after which meets . Also, find the total distance travelled by .


Important Questions on Kinematics
A large heavy box is sliding without friction down a smooth plane of inclination . From a point on the bottom of the box, a particle is thrown inside the box. The initial speed of the particle with respect to the box is and the direction of projection makes an angle with the bottom as shown in the figure.
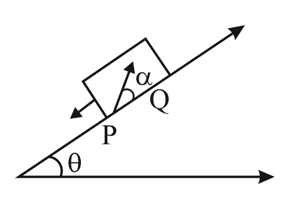
(a) Find the distance along the bottom of the box between the point of projection and the point where the particle lands (assume that the particle does not hit any other surface of the box. Neglect air resistance).
(b) If the horizontal displacement of the particle as seen by an observer on the ground is zero. Find the speed of the box with respect to the ground at the instant when the particle was projected.
An insect moves in a circular path of radius . If it rotates through an angle , find its displacement, , where, is the change in position vector.