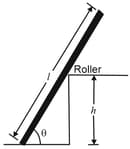
In the figure shown below, a uniform plank, with a length of and a weight of , rests on the ground and against a frictionless roller, at the top of a wall of height . The plank remains in equilibrium for any value of but slips if . Find the coefficient of static friction between the plank and the ground. (Take and )


Important Questions on Equilibrium and Elasticity
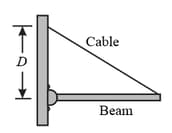
In the figure shown below, a cable of negligible mass suspends one end of a horizontal beam of weight and length. The beam's other end is hinged to a wall. The cable's tension is . (a) What is distance between the hinge and the cable's attachment point on the wall? (b) If was more, would the cable tension be more, less or the same?
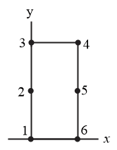
Because varies so little over the extent of most structures, any structure's center of gravity effectively coincides with its center of mass. Here is a fictitious example where varies more significantly. Figure given below shows an array of six particles, each with mass , fixed to the edge of a rigid structure of negligible mass. The distance between adjacent particles along the edge is . The following table gives the value of at each particle's location. Using the coordinate system shown, find (a) the coordinate, and (b) the coordinate, of the center of mass of the six-particle system. Then find (c) the coordinate, and (d) the coordinate, of the center of gravity of the six-particle system.
| Particle |
Particle |
||
In the figure shown below , a uniform log hangs by two steel wires, and , both of radius . Initially, wire was long and shorter than wire . The log is now horizontal. What are the magnitudes of the forces on it from (a) wire and (b) wire ? (c) What is the ratio ? (Young's modulus of steel )
In the figure shown below, uniform beams and are attached to a wall with hinges and loosely bolted together (there is no torque of one on the other). Beam has length and mass , and beam has mass . The two hinge points are separated by distance . In unit-vector notation, what is the force on (a) beam due to its hinge, (b) beam due to a bolt, (c) beam due to its hinge, and (d) beam due to the bolt?
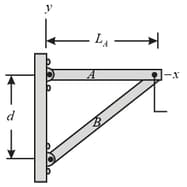
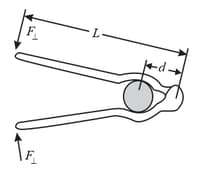
Figure below is an overhead view of a rigid rod that turns about a vertical axle until the identical rubber stoppers and are forced against rigid walls at distances from the axle. Initially the stoppers touch the walls without being compressed. Then force of magnitude is applied perpendicular to the rod at a distance from the axle. Find the magnitude of the force compressing (a) stopper and stopper .

