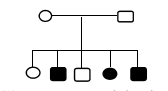
In the given pedigree, circles represent females and squares represent males. Filled shapes indicate affected individuals for a particular trait, while unfilled shapes indicate unaffected individuals. Carrier status is not shown in the pedigree. Study the following statements about this pedigree and choose the correct option(s).
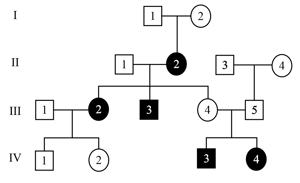
Statement 1- Trait follows -linked recessive mode of inheritance.
Statement 2- Trait follows -linked dominant mode of inheritance.
Statement 3- Trait follows autosomal recessive mode of inheritance.
Statement 4- Individual II-1 is a carrier for the trait.
Statement 5- Individual III- 4 is a carrier for the trait.
Statement 6- Individual I-1 is a carrier for the trait.

Statement 2- Trait follows -linked dominant mode of inheritance.
Statement 3- Trait follows autosomal recessive mode of inheritance.
Statement 4- Individual II-1 is a carrier for the trait.
Statement 5- Individual III- 4 is a carrier for the trait.
Statement 6- Individual I-1 is a carrier for the trait.
Important Questions on Principles of Inheritance and Variation
The following two pedigrees describe the autosomal genetic disorders and in Family and Family , respectively.
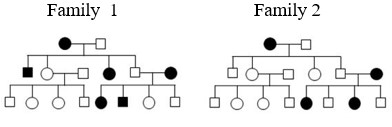
Choose the CORRECT statement from the following options.
(i) Haemophilia is a sex-linked recessive disease.
(ii) Down's syndrome is due to aneuploidy.
(iii) Phenylketonuria is an autosomal recessive gene disorder.
(iv) Sickle cell anaemia is an X-linked recessive gene disorder.
From the following, find out the symbol used in the human pedigree analysis representing males.
The following question has four choices. Choose the best option.
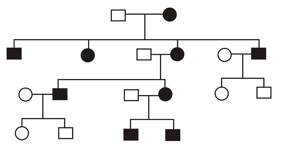
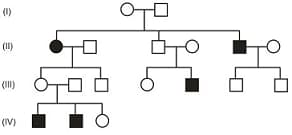
In the given pedigree chart, the trait shown is :
Reason (R): Pedigree is a chart showing record of inheritance of certain traits over two or more ancestral generations of a person.
| Group I | Group II |
| P. Phenylketonuria | i. Melanin synthesis |
| Q. Albinism | ii. Conversion of Phenylalanine to Tyrosine |
| R. Homocystinuria | iii. Tyrosine degradation |
| S. Argininemia | iv. Methionine metabolism |
| v. Urea Synthesis |
A woman heterozygous for colour blindness marries a colour-blind man. What would be the ratios of carrier daughters, colour-blind daughters, normal sons, and colour-blind sons in the F1 generation?
The diagram below represents the pedigree of a certain genetic disease (affected individuals are shaded). What is the mode of inheritance of the gene responsible for this disease?