In the sea, the main nitrogen-fixing organisms are blue-green algae which float near the top of the water in the plankton. Construct a diagram or chart similar.

Important Questions on Organisms and their Environment
The graph below shows population changes over one summer, for two insects. One is a type of greenfly, and the other is a ladybird which feeds on it.
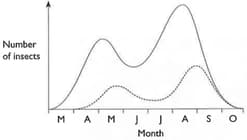
(a) Which curve represents the ladybird population, and which the greenfly population and give a reason for your answer.
The graph below shows population changes over one summer, for two insects. One is a type of greenfly, and the other is a ladybird which feeds on it.
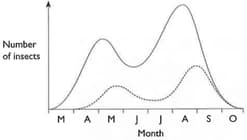
Explain why the two curves are similar? Why do the two curves rise and fall at slightly different times?
The diagram below shows what happens to energy as it passes through an herbivorous mammal (a wildebeest).
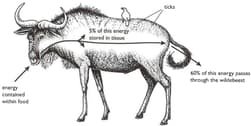
State the source of the energy in the food eaten by the wildebeest.
The diagram below shows what happens to energy as it passes through an herbivorous mammal (a wildebeest).
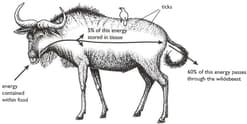
State the form in which the energy is present in the carbohydrate eaten by the wildebeest.
The diagram below shows what happens to energy as it passes through an herbivorous mammal (a wildebeest).
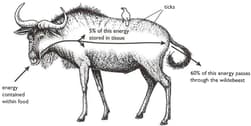
Name the process that makes the remaining of the energy in the food available to the wildebeest.
The diagram below shows what happens to energy as it passes through an herbivorous mammal (a wildebeest).
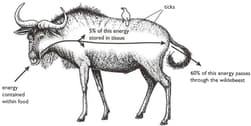
State three ways in which the energy may be used within the wildebeest.
The bird on the wildebeests back is an oxpecker that feeds both on blood-sucking parasites (ticks) living on the wildebeest, and on blood from the wildebeests wounds.
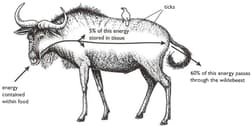
Draw a food web to show the feeding relationships of the organisms in the diagram.
The bird on the wildebeests back is an oxpecker that feeds both on blood-sucking parasites (ticks) living on the wildebeest, and on blood from the wildebeests wounds.
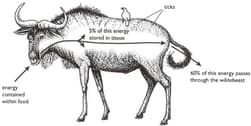
Explain why there must always be fewer oxpeckers than ticks in this food web.
