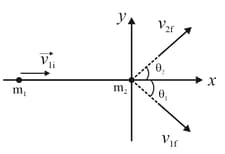
In two-dimensional collision, in the figure shown below, the projectile particle has mass initial speed and final speed . The initially stationary target particle has mass and final speed . The projectile is scattered at an angle given by . (a) Find the angle . (b) Find in terms of . (c) Is the collision elastic?


Important Questions on Center of Mass and Linear Momentum
A force acts on two particles of masses and moving at the same speed but at right angles to each other, as shown in figure shown below. The force acts on both the particles for a time . Consequently, the particle of mass moves with a velocity in its original direction. The force acts in direction,
(a) Find the new velocity of the other particle.
(b) Also find the change in the kinetic energy of the system.

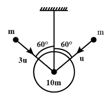
In figure shown below a bob of mass is suspended from an inextensible string with negligible mass. When the bob is in equilibrium (at rest), two particles each of mass m strike it simultaneously with the speeds indicated. The particles stick to the bob. Find (a) the magnitude of the net impulse on the string due to the collision,
(b) the velocity of the system just after the collision, and (c) the mechanical energy lost in the collision.
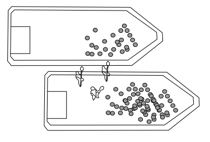
In figure shown below two long barges are moving in the same direction in still water, one with a speed of and the other with a speed of While they are passing each other, coal is shoveled from the slower to the faster one at a rate of . How much additional force must be provided by the driving engines of (a) the faster barge and (b) the slower barge if neither is to change speed? Assume that the shoveling is always perfectly sideways and that the frictional forces between the barges and the water do not depend on the mass of the barges.
Consider a rocket that is in deep space and at rest relative to an inertial reference frame. The rocket's engine is to be fired for a certain interval. What must be the rocket's mass ratio (ratio of initial to final mass) over that interval if the rocket's original speed relative to the inertial frame is to be equal to (a) the exhaust speed (speed of the exhaust products relative to the rocket) and
(b) times the exhaust speed? [ Use where is Euler's number ]
A rocket that is set for a vertical launch has a mass of and contains of fuel. The rocket can have a maximum exhaust velocity of . What should be the minimum rate of fuel consumption (a) to just lift it off the launching pad and (b) to give it an acceleration of (c) If the consumption rate is set at what is the rocket speed at the moment when the fuel is fully consumed? [ Use ]
