Inside a uniformly charged ball, at , the electric field is maximum. Then (Given, is volume charge density)

Important Questions on Electric Charges and Fields
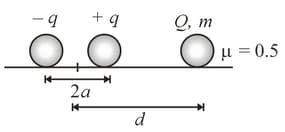
A dipole having charges and is fixed on a rough surface as shown. Another charge of mass is placed at distance from this dipole. The minimum value of for which charge will not move. (Given , co-efficient of static friction )
Two balls of charges and initially have exactly same velocity. Both the balls are, subjected to same uniform electric field for same time. As a result, the velocity of the first ball is reduced to half of its initial value and its direction changes by The direction of the velocity of second ball is found to change by
The electric field and initial velocity of the charged particle are inclined at angle
Two balls of charges and initially have exactly same velocity. Both the balls are, subjected to same uniform electric field for same time. As a result, the velocity of the first ball is reduced to half of its initial value and its direction changes by The direction of the velocity of second ball is found to change by
If new velocity of second charged particle has a magnitude times the initial velocity, then is
There is a non-conducting rod of length and negligible mass with two small balls each of mass and electric charge attached to its ends. The rod can rotate in the horizontal plane about a fixed vertical axis crossing it a distance from one of its ends. A uniform horizontal electric field (along axis) is established. At first the rod is in unstable equilibrium. In what position, the rod must be set so that if displaced a little from that position, it begins simple harmonic oscillations about the axis?
