Leidenfrost effect. A water drop will last about on a hot skillet with a temperature between and about . However, if the skillet is much hotter, the drop can last several minutes, an effect named after an early investigator. The longer lifetime is due to the support of a thin layer of air and water vapour that separates the drop from the metal (by distance in Fig.). Let and assume that the drop is flat with height and bottom face area Also assume that the skillet has a constant temperature and the drop has a temperature of Water has density and the supporting layer has a thermal conductivity
At what rate is energy conducted from the skillet to the drop through the drop's bottom surface?
If conduction is the primary way energy moves from the skillet to the drop, how long will the drop last?



Important Questions on Temperature, Heat, and the First Law of Thermodynamics
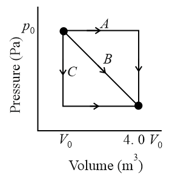
In given Fig. a gas sample expands from to while its pressure decreases from to If and , how much work is done by the gas if its pressure changes with volume via path and path
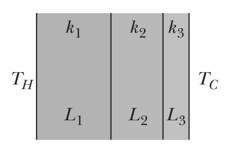
Given figure shows the cross-section of a wall made of three layers. The layer thicknesses are , , and . The thermal conductivities are , , and . The temperatures at the left side and right side of the wall are and respectively. Thermal conduction is steady. What is the temperature difference across layer (between the left and right sides of the layer)? If were instead equal to , would the rate at which energy is conducted through the wall be greater than, less than, or the same as previously, and what would be the value of
Consider the slab shown in the figure. Suppose that and the material is copper. If ,, and a steady state is reached, find the conduction rate through the slab.[ thermal conductivity of copper is ]