EASY
Earn 100
Light of certain frequency and intensity incident on a photosensitive material causes photoelectric effect. If both the frequency and intensity are doubled, the photoelectric saturation current becomes
(a)halved
(b)quadrupled
(c)unchanged
(d)doubled
28.57% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
MEDIUM
When a certain metallic surface is illuminated with monochromatic light of wavelength the stopping potential for photoelectric current is and when the same surface is illuminated with light of wavelength the stopping potential is The threshold wavelength of this surface for photoelectric effect is
MEDIUM
In a photoelectric effect measurement, the stopping potential for a given metal is found to be when radiation of wavelength is used. If radiation of wavelength is used with the same metal then the stopping potential (in ) will be
EASY
Maximum kinetic energy of a photoelectric varies with the frequency of the incident radiation as
MEDIUM
When the light of frequency (where is threshold frequency), is incident on a metal plate, the maximum velocity of electrons emitted is . When the frequency of the incident radiation is increased to the maximum velocity of electrons emitted from the same plate is The ratio of is
HARD
In a historical experiment to determine Planck's constant, a metal surface was irradiated with light of different wavelengths. The emitted photoelectron energies were measured by applying a stopping potential. The relevant data for the wavelength of incident light and the corresponding stopping potential are given below:
| 0.3 | 2.0 |
| 0.4 | 1.0 |
| 0.5 | 0.4 |
Given that Planck's constant (in units of ) found from such an experiment is :
MEDIUM
Photons of wavelength are incident on a metal. The most energetic electrons ejected from the metal are bent into a circular are of radius R by a perpendicular magnetic field having a magnitude B. The work function of the metal is (Where symbols have their usual meanings).
MEDIUM
Light of wavelength is incident on a metal with work function . The de Broglie wavelength of the emitted electron is:
MEDIUM
A laser light of wavelength is used to weld Retina detachment. If a laser pulse of width and power is used, the approximate number of photons in the pulse are (Take Planck's Constant,
MEDIUM
Light of wavelength is incident on a metal with work function The de Broglie wavelength of the emitted electron is:
HARD
A metal plate of area is illuminated by a radiation of intensity . The work function of the metal is The energy of the incident photons is and only of it produces photo electrons. The number of emitted photo electron per second and their maximum energy, respectively, will be:
MEDIUM
On a photosensitive material, when the frequency of incident radiation is increased by , the kinetic energy of emitted photoelectrons increases from to . The work function of the surface is
MEDIUM
Following graphs show the variation of stopping potential corresponding to the frequency of incident radiation for a given metal. The correct variation is shown in graph ( Threshold frequency)
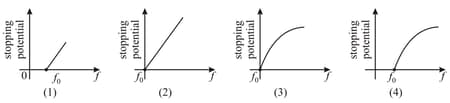
EASY
The electric field of certain radiation is given by the equation falls in a metal surface having work function The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons is [Planck's constant and electron charge ]
MEDIUM
Photons with energy of are incident on a cathode, in a photoelectric cell. The maximum energy of emitted photoelectrons is When photons of energy are incident on , no photoelectrons will reach the anode, , if, the stopping potential of relative to is
MEDIUM
The maximum velocity of the photoelectrons emitted from the surface is when light of frequency falls on a metal surface. If the incident frequency is increased to , the maximum velocity of the ejected photoelectrons will be:
MEDIUM
Photons of energy are incident on two metals and with work functions and , respectively. The minimum de-Broglie wavelengths of the emitted photoelectrons with maximum energies are and , respectively, where is nearly,
MEDIUM
In a photocell circuit, the stopping potential, is a measure of the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons. The following graph shows experimentally measured values of stopping potential versus frequency, of incident light.
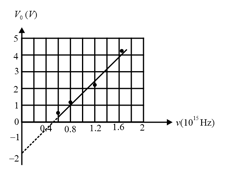
The values of Planck's constant and the work function as determined from the graph are (taking the magnitude of electronic charge to be,),
HARD
The magnetic field associated with a light wave is given, at the origin, by If this light falls on a silver plate having a work function of what will be the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons?
MEDIUM
When a metallic surface is illuminated with radiation of wavelength , the stopping potential is . If the same surface is illuminated with radiation of wavelength , the stopping potential is . The threshold wavelength for the metallic surface is:
MEDIUM
The surface of certain metal is first illuminated with light of wavelength and then, by a light of wavelength It is found that the maximum speed of the photoelectrons in the two cases differ by a factor of . The work function of the metal (in ) is close to
(Energy of photon )

