Lung volume is also called respiratory volume. An instrument called a Spirometer helps in measuring Respiratory volumes.
Important Questions on Respiratory System
The graph shows how a student’s breathing rate changed during and after exercise.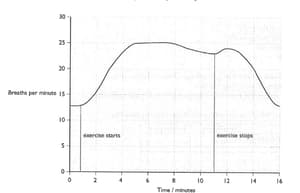
Describe and explain how would you expect the student's heart rate to change during the 16-minute period shown on the graph.
The graph shows how a student’s breathing rate changed during and after exercise.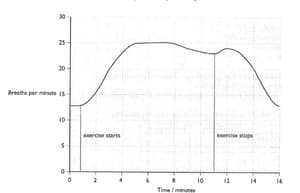
Calculate the increase in the student’s breathing rate from when he started to do exercise, to its maximum rate.
The graph shows how a student’s breathing rate changed during and after exercise.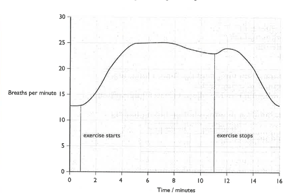
Calculate how long it took after he finished his exercise for his breathing to return to normal.
A girl breathed into a machine that recorded the volume of the air that she breathed in and out. The results were recorded as a graph of volume against time. The diagrams show results obtained when she was resting and when she was exercising. 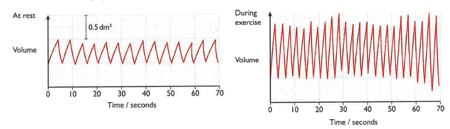
Use the second graph to find the volume of the first breath that she took while she was exercising.(Remember to include the unit in your answer)
A girl breathed into a machine that recorded the volume of the air that she breathed in and out. The results were recorded as a graph of volume against time. The diagrams show results obtained when she was resting and when she was exercising. 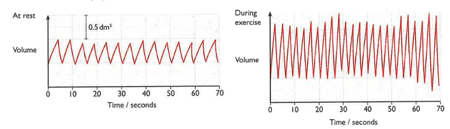
Use the first graph to find the volume of the first breath that she took while she was resting.(Remember to include the unit in your answer)
A girl breathed into a machine that recorded the volume of the air that she breathed in and out. The results were recorded as a graph of volume against time. The diagrams show results obtained when she was resting and when she was exercising. 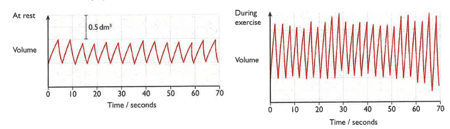
Describe the mechanism that brought these changes in the rate and depth of breathing helped the girl's body.
The graph shows how a student’s breathing rate changed during and after exercise.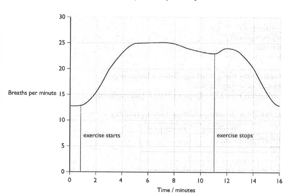
Explain why his breathing rate does not return to normal immediately after he stopped exercise.
(i) Inspiratory Capacity (IC) = Tidal Volume + Residual Volume
(ii) Vital Capacity (VC) = Tidal Volume (TV) + Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV) + Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV)
(iii) Residual Volume (RV) = Vital Capacity (VC) - Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV)
(iv) Tidal Volume (TV) = Inspiratory Capacity (IC) - Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV) Codes
A girl breathed into a machine that recorded the volume of the air that she breathed in and out. The results were recorded as a graph of volume against time. The diagrams show results obtained when she was resting and when she was exercising. 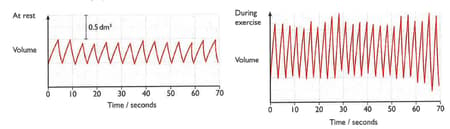
Use the first graph to find how many breaths per minute the girl took while she was resting.
A girl breathed into a machine that recorded the volume of the air that she breathed in and out. The results were recorded as a graph of volume against time. The diagrams show results obtained when she was resting and when she was exercising. 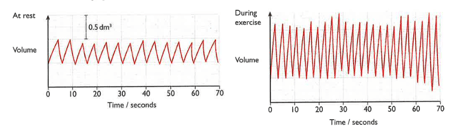
Use the second graph to find how many breaths per minute the girl took while she was resting.
The volume of air in the lungs and the rate at which it is exchanged during inspiration and expiration was measured.
The following diagram shows a group of lung volume and capacities:
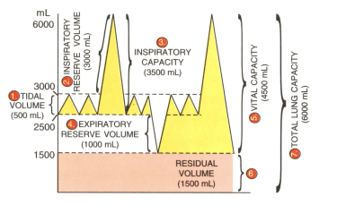
Study the diagram carefully and explain briefly the following:
(a) Tidal volume
(b) Inspiratory reserve volume
(c) Expiratory reserve volume
(d) Vital capacity
(e) Residual volume

