Match column with column and select the correct option from the codes given below.
Column I
Column II
(a)
Saddle joint
(i)
Metacarpo-phalangeal joint
(b)
Gliding joint
(ii)
Carpo-metacarpal joint of thumb
(c)
Hinge
(iii)
Between tarsal bones
(d)
Ellipsoid joint
(iv)
Knee joint

Important Questions on Locomotion and Movement
Consider the following statements each with one or two blanks.
| (i) | Each pectoral girdle consists of a (A) and a (B) |
| (ii) | (C) is a condition of rapid spasms (wild contractions) in muscle due to low in body fluid. |
| (iii) | Each organized skeletal muscle in our body is made of a number of (D) held together by a common collagenous connective tissue layer called (E). |
Which one of the following options correctly fills the blanks in any two of the statements?
Which of the following is the correct pairing regarding a specific disorder of muscular or skeletal system?
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: Inflammation of a skeletal joint may immobilise the movements of the joint.
Statement 2: This may be caused due to uric acid crystals in the joint cavity and ossification of articular cartilage.
Refer to the given graph carefully and answer the following question.
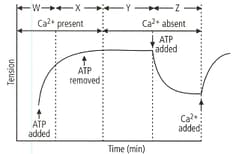
Which of the labelled parts on the graph represents rigor mortis?
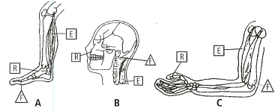
Refer to the given figures, and arrange them in an order of first-class lever, second-class lever, and third-class lever.
The given graph shows the length-tension curve for a typical vertebrate sarcomere.
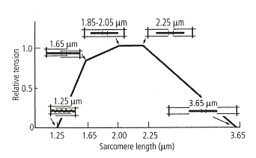
By analysing the graph, what can you deduce regarding muscle contraction?
(i) Neither the myosin filaments nor the actin thin filaments change in length when a sarcomere shortens or is stretched. Instead, it is the extent of overlap between actin and myosin filaments that changes.
(ii) The total tension produced by a sarcomere is proportional to the total number of cross-bridges that can interact with actin filaments, and this number, in turn, is proportional to the amount of overlap between thick and thin filaments.
(iii) The tension produced by the muscle is maximal when the overlap between thick and thin filaments allows the largest number of myosin cross-bridges to bind to actin.
(iv) Tension drops off with increased length because the thick and thin filaments overlap less and fewer cross-bridges can bind.
(v) Tension drops off with decreased length because thin filaments at the two ends of the sarcomere begin to collide with each other, preventing further shortening.
