EASY
Earn 100
Name that branch of science which deals with the study of Earth.
50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Physical World
EASY
A total solar eclipse is observed from the earth. At the same time an observer on the moon views the earth. She is most likely to see ( denotes the earth)
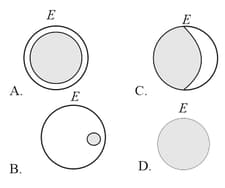
EASY
HARD
| Technology | Scientific principle |
| 1. Steam engine | A- Propagation of e.m wave |
| 2. Nuclear reactor | B- Newtons law of motion |
| 3. Radio and TV | C- superconductivity |
|
4. Computers |
D- Role of DNA in heredity |
| 5. Lasers | E- Thermodynamics |
| 6. Ultra-high magnetic fields | F- Faraday law of induction |
| 7. Rocket propulsion | G- Conversion of gravitational potential energy into electrical energy |
| 8. Genetic engineering | H- Motion of charge particle into an electric field |
| 9. Electric generators | I- Fission of uranium by slow neutrons |
| 10. Hydroelectric power | J- Amplification by population inversion |
| 11. Aeroplanes | K- Digital logic of the electronic circuit |
| 12. Particle accelerator | L- Bernoulli's principle in fluid dynamic |
| 13. Photocell | M- Thin-film optical interference |
| 14. Electron microscope | N- Reflection of ultrasonic waves |
| 15. Non-reflecting coating | O- Total internal reflection in light |
| 16. Optical fibre | P- Photoelectric effect |
| 17. Sonar | Q- Wave nature of electron |
HARD
| Scientist | Discovery / contribution |
| (i) J.C. Bose | (a) Thermal ionization |
| (ii) C.V. Raman | (b) Cosmic radiation and nuclear weapons |
| (iii) M.N.Saha | (c) Quantum statistics |
| (iv) S.N. Bose | (d) Ultrasonic radio waves |
| (v) H.J.Bhabha | (e) Structure and evolution of stars |
| (vi) S. Chandrashekhar | (f) Inelastic scattering of light by molecules. |
EASY
EASY
HARD
Match the scientist with contribution/ discovery
| Scientist | Contribution/ discovery |
| (i) Faraday | (a) Law of gravitation |
| (ii) Rutherford | (b) Quantum model of hydrogen |
| (iii) Chadwick | (c) Unification of light and electromagnetism |
| (iv) Bohr | (d) Theory of relativity, explanation of photoelectric effect |
| (v) Newton | (e) x-rays |
| (vi) Maxwell | (f) Unification of weak and electromagnetic interaction |
| (vii) Salaam | (g) Law of electromagnetic induction |
| (viii) Einstein | (h) Expansion of universe |
| (ix) Roentgen | (i) Neutron |
| (x) Madam Curie | (j) Nuclear model of atom |
| (xi) J.J. Thomson | (k) Wave nature of light |
| (xii) de Broglie | (l) Transistor |
| (xiii) John Bardeen | (m) Electron |
| (xiv) Hubble | (n) Discovery of radium |
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM

