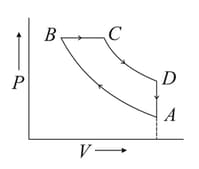
One mole of a diatomic ideal gas is taken through a cyclic process starting from point . The process is an adiabatic compression. is isobaric expansion. an adiabatic expansion and is isochoric as shown in P-V diagram. The volume ratios are and the temperature at is . Calculate the temperature of the gas at the points and and find the efficiency of the cycle.


Important Questions on Thermodynamics
One mole of an ideal monoatomic gas is taken around the cyclic process as shown in the figure. Calculate,
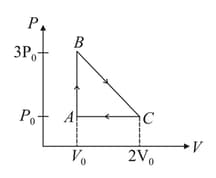
(a) the work done by the gas
(b) the heat rejected by the gas in the path and the heat absorbed by the gas in the path
(c) the net heat absorbed by the gas in the path
(d) the maximum temperature attained by the gas during the cycle.
Two moles of a monatomic gas, initially at pressure and volume , undergo an adiabatic compression until its volume becomes . Then the gas is given heat at constant volume .
(a) Sketch the complete process on a diagram.
(b) Find the total work done by the gas, the total change in its internal energy and the final temperature of the gas.
In given figure, an adiabatic cylindrical tube of volume is divided in two equal parts by a frictionless adiabatic separator. An ideal gas in left side of a tube having pressure and temperature , where as on the right side having pressure and temperature is the same for both the gases. The separator is slid slowly and is released at a position where it can stay in equilibrium. Find (a) the final volumes of the two parts, (b) the heat given to the gas in the left part and (c) the final common pressure of the gases.

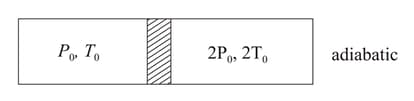
A cylindrical tube with adiabatic walls having volume contains an ideal monoatomic gas as shown in figure. The tube is divided into two equal parts by a fixed super conducting wall. Initially, the pressure and the temperature are on the left and on the right. When system is left for sufficient amount of time the temperature on both sides becomes equal (a) Find work done by the gas on the right part? (b) Find the final pressures on the two sides. (c) Find the final equilibrium temperature. (d) How much heat has flown from the gas on the right to the gas on the left?
An ideal gas having initial pressure and volume .
(a) The gas is taken isothermally to a pressure and then adiabatically to a pressure . Find the final volume.
(b) The gas is brought back to its initial state. It is adiabatically taken to a pressure and then isothermally to a pressure . Find the final volume.
