EASY
Earn 100
Point out the differences between the free oscillation and forced oscillation.
Important Questions on Sound
HARD
EASY
Two pendulums and are suspended from a wire as shown in the given figure. Pendulum is made to oscillate by displacing it from its mean position. It is seen that also starts oscillating. If the length of is made equal to , then what difference will you notice in the oscillations of ?
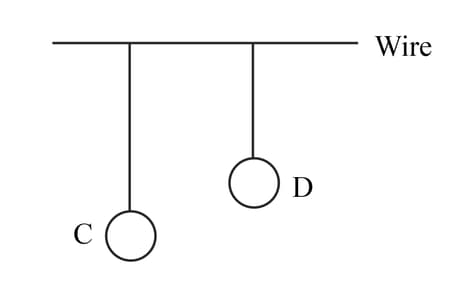
EASY
EASY
Two pendulums and are suspended from a wire as shown in the given figure. Pendulum is made to oscillate by displacing it from its mean position. It is seen that also starts oscillating. Name the type of oscillation, will execute.
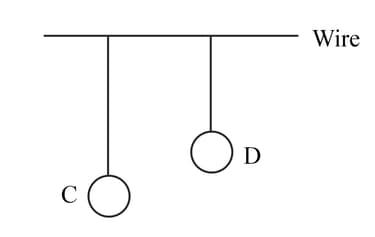
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
Describes the oscillatory motion of body in a dissipative medium under the influence of a periodic force, then the state of maximum amplitude of the oscillation is a phenomena of
MEDIUM
free vibrations
damped vibrations
maintained vibrations
forced vibrations
HARD
EASY
EASY
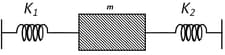
HARD
If the amplitude of the particle is maximum for and the energy of the particle is maximum for then
EASY
MEDIUM
HARD
EASY
MEDIUM
HARD
EASY

