Proceeding from Fermat's principle, derive the refraction formula for paraxial rays on a spherical boundary surface of radius , between media with refractive indices and .

Important Questions on OPTICS
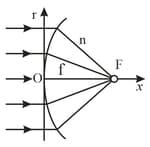
A parallel beam of light falls from vacuum on a surface enclosing a medium with refractive index (figure). Find the shape of that surface if the beam is brought into focus at the point at a distance from the crest . What is the maximum radius of a beam that can still be focused?
the transverse magnification, if the curvature radius of the lens' convex surface is ;
the image illuminance, if the luminance of the object is and the entrance aperture diameter of the lens is and losses of light are negligible.
of a thin glass lens, in a liquid with refractive index and refractive index of glass in air is , if its optical power in air is ;
of a thin symmetrical biconvex glass lens, with air on one side and water on the other side, if the optical power of that lens in air is .
By means of plotting, find
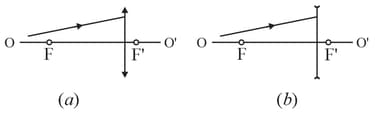
the path of a ray of light beyond thin converging and diverging lenses (where is the optical axis, and are the front and rear focal points);
the position of a thin lens and its focal points, if the position of the optical axis and the positions of the conjugate points (see figure) are known; the media on both sides of the lenses are identical;
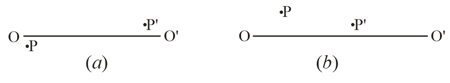
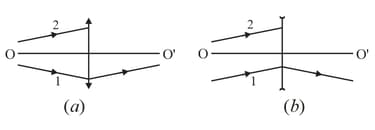
the path of ray beyond the converging and diverging lenses (Figure), if the path of ray and the positions of the lens and of its optical axis are all known; the media on both sides of the lenses are identical.
the distance between the two positions of the lens is ,
the transverse dimensions of the image at one position of the lens are greater than those at the other position.
