EASY
NEET
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
Stele includes
88.89% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Anatomy of Flowering Plants
EASY
NEET
IMPORTANT
Isobilateral leaves have
EASY
NEET
IMPORTANT
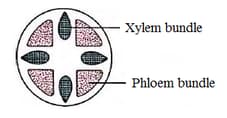
EASY
NEET
IMPORTANT
EASY
NEET
IMPORTANT
MEDIUM
NEET
IMPORTANT
| I | II | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | Bulliform cells | (i) | Regulate opening and cells closing of stomata |
| (b) | Guard cells | (ii) | Aerating pores in the bark of plant |
| (c) | Lenticels | (iii) | Rolling in and out of leaves |
| (d) | Subsidiary cells | (iv) | Accessory cells |
EASY
NEET
IMPORTANT
EASY
NEET
IMPORTANT
EASY
NEET
IMPORTANT
