Strontium sulphate is mixed with conc. and flame test is performed. The colour of flame is

Important Points to Remember in Chapter -1 - Principles of Qualitative Analysis from Embibe Experts Gamma Question Bank for Engineering Chemistry Solutions
1. Charcoal Cavity Test:
|
Observation |
Inference | |
|
Incrustation or Residue |
Metallic bead |
|
|
Yellow when hot, white when cold |
None |
|
|
Brown when hot, yellow when cold |
Grey bead which marks the paper |
|
|
No characteristic residue |
Red beads or scales |
|
|
White residue which glows on heating |
None |
|
|
Black |
None |
Nothing definite-generally coloured salt |
2. Cobalt Nitrate Test:
| S. No. | Metal | Colour of the mass |
| 1. | Zinc | Green |
| 2. | Aluminium | Blue |
| 3. | Magnesium | Pink |
| 4. | Tin | Bluish – green |
3. Flame Test:
| Colour of Flame |
Inference |
| Crimson Red / Carmine Red |
Lithium |
| Golden yellow |
Sodium |
| Violet / Lilac |
Potassium |
| Brick red |
Calcium |
| Apple Green / Yellowish Green |
Barium |
| Green with a Blue centre/Greenish Blue |
Copper |
4. Borax Bead Test:
| Metal | Colour in oxidising flame | Colour in reducing flame | ||
| When Hot | When Cold | When Hot | When Cold | |
| Copper | Green | Blue | Colourless | Brownish red |
| Iron | Brownish yellow | Pale yellow / Yellow | Bottle green | Bottle green |
| Chromium | Yellow | Green | Green | Green |
| Cobalt | Blue | Blue | Blue | Blue |
| Manganese | Violet / Amethyst | Red / Amethyst | Grey/Colourless | Grey / Colourless |
| Nickel | Violet | Brown/Reddish brown | Grey | Grey |
5. Analysis of ANIONS (Acidic Radicals):
(i) Dilute sulphuric acid/dilute hydrochloric acid group:
(a) Carbonate ion :
Dilute test: A colourless odourless gas is evolved with brisk effervescence.
Lime water/Baryta water test:
(b) Sulphite ion :
Dilute test:
; has suffocating odour of burning sulphur.
Acidified potassium dichromate test: The filter paper dipped in acidified turns green.
Barium chloride/Strontium chloride solution:
White precipitate dissolves in dilute .
(c) Sulphide ion :
Dilute test: Pungent smelling gas like that of rotten egg is obtained.
Lead acetate test:
Sodium nitroprusside test: Purple coloration is obtained.
Cadmium carbonate suspension/ Cadmium acetate solution:
(d) Nitrite ion :
Dilute test:
;
Starch iodide test:
(starch iodine adsorption complex)
(e) Acetate ion
Dilute test:
Neutral ferric chloride test:
(ii) Conc. GROUP:
(a) Chloride ion :
Concentrated test:
Silver nitrate test:
White precipitate is soluble in aqueous ammonia and precipitate reappears with .
;
Chromyl chloride test:
;
(b) Bromide ion :
Concentrated test:
;
Silver nitrate test:
Yellow precipitate is partially soluble in dilute aqueous ammonia but readily dissolves in concentrated ammonia solution.
Chlorine water test (organic layer test):
dissolve to give reddish brown colour in organic layer.
(c) Iodide ion :
Concentrated test:
(pungent smelling dark violet)
Starch paper test:
Iodides are readily oxidised in acid solution to free iodine; the free iodine may than be identified by deep blue colouration produced with starch solution.
.
Silver nitrate test:
Bright yellow precipitate is formed.
Bright yellow precipitate is insoluble in dilute aqueous ammonia but is partially soluble in concentrated ammonia solution.
Chlorine water test (organic layer test):
dissolves to give violet colour in organic layer.
(d) Nitrate ion
Concentrated test:
Pungent smelling reddish-brown vapours are evolved.
Addition of bright copper turnings or paper pellets intensifies the evolution of reddish-brown gas.
;
.
Brown ring test:
.
.
(iii) Miscellaneous Group:
(a) Sulphate ion :
Barium chloride test:
.
White precipitate is insoluble in warm dil. as well as but moderately soluble in boiling concentrated hydrochloric acid.
Lead acetate test:
White precipitate soluble in excess of hot ammonium acetate
(b) Phosphate ion :
Ammonium molybdate test:
6. Analysis of cations:
Group 0: Ammonium ion :
Nessler's reagent test (Alkaline solution of potassium tetraidomercurate :
7. GROUP :
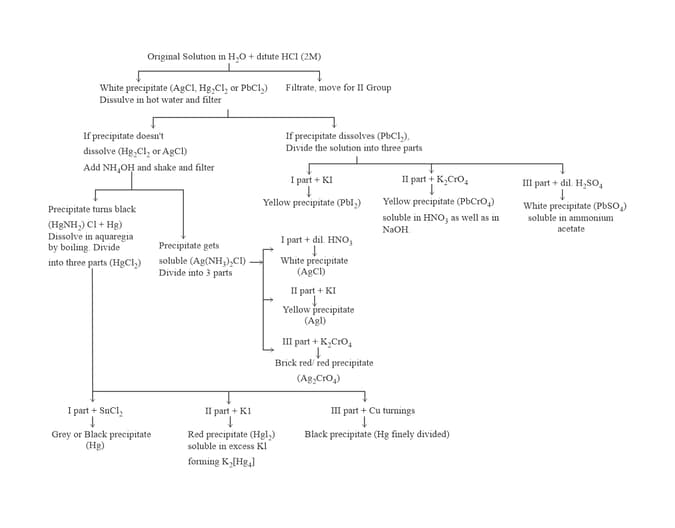
8. GROUP
:
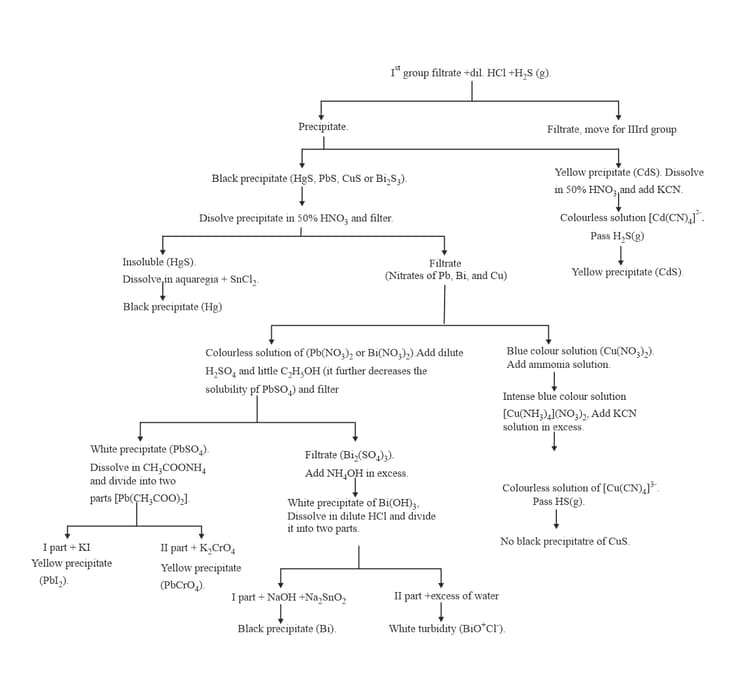
9. GROUP :
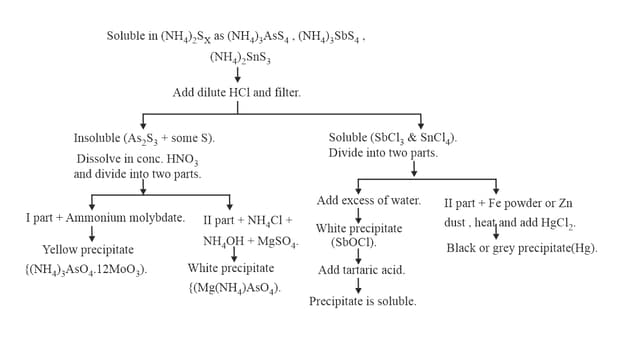
10. GROUP :
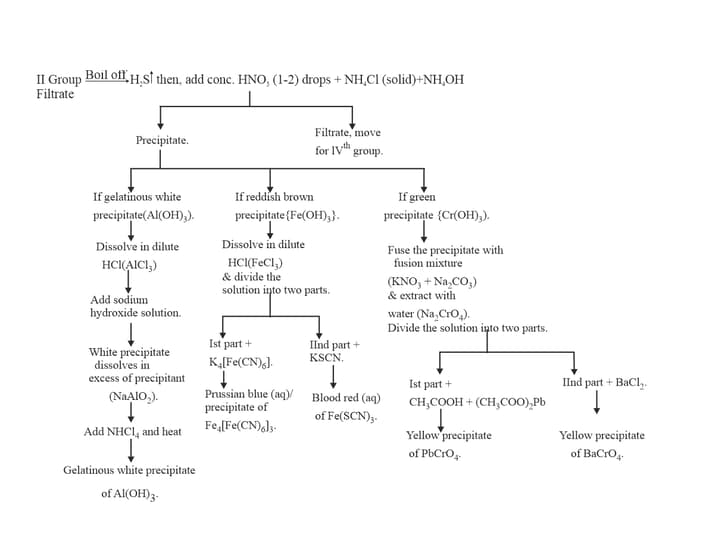
11. GROUP :
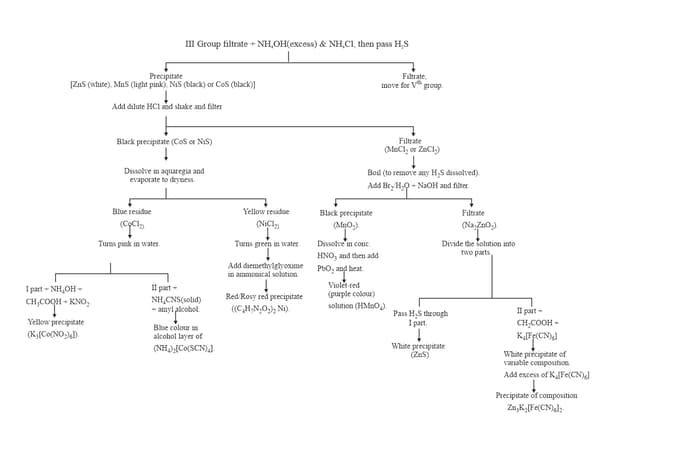
12. GROUP :
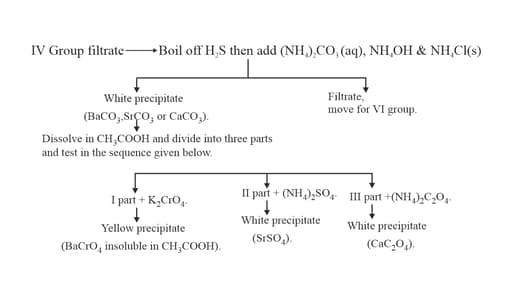
13. GROUP:
(i) MAGNESIUM ION :
(ii) Titan Yellow (a water-soluble yellow dyestuff): It is adsorbed by producing a deep red colour or precipitate.
