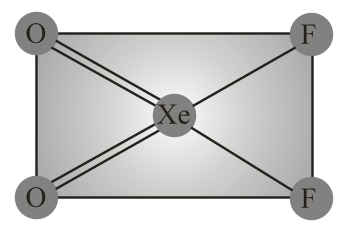
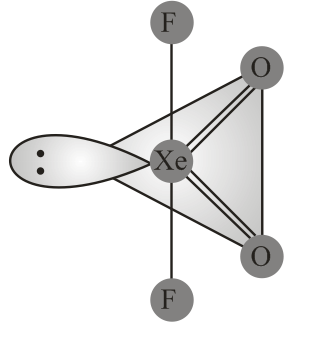
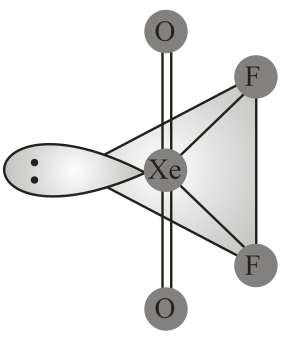
Structure of is correctly represented by

Important Points to Remember in Chapter -1 - The p-Block Elements from Embibe Experts Gamma Question Bank for Engineering Chemistry Solutions
1. The p-block elements:
The p-block elements consist of elements of groups having as valence shell electronic configuration where .
2. Group 15 elements (Nitrogen Family)
(i) Elements:
(ii) Electronic configuration:
(iii) Oxidation state: oxidation state is favoured by heavier elements due to ‘inert pair effect’.
(iv) Nitrogen differs from other elements of group due to small size, formation of multiple bonds with itself and with highly electronegative atom like and non-availability of d orbitals to expand its valence shell.
(v) Nitrogen forms oxides in various oxidation states: and . These oxides have resonating structures and have multiple bonds.
(vi) Ammonia can be prepared on large scale by Haber’s process.
(vii) is a strong monobasic acid and is a powerful oxidising agent. Metals and non-metals react with under different conditions to give or .
(viii) Phosphorus exists as in elemental form. It exists in several allotropic forms. It forms hydride, which is a highly poisonous gas. It forms two types of halides as and .
(ix) is prepared by the reaction of white phosphorus with dry chlorine and is prepared by the reaction of phosphorus with .
(x) Phosphorus forms a number of oxoacids. Depending upon the number of groups, their basicity varies. The oxoacids which have bonds are good reducing agents.
3. Group 16 elements (Oxygen Family - Chalcogens)
(i) Elements:
(ii) Electronic configuration:
(iiI) Maximum oxidation state of .
(iv) Dioxygen is prepared by heating in presence of . It forms a number of oxides with metals. Allotropic form of oxygen is which is a highly oxidising agent.
(v) Sulphur combines with oxygen to give oxides such as and . is prepared by the reaction of sulphur with oxygen. It is used in the manufacture of .
(vi) Sulphur forms a number of oxoacids. Amongst them, the most important is . It is prepared by contact process. It is a dehydrating and oxidising agent. It is used in the manufacture of several compounds.
4. Group 17 elements (Halogens)
(i) Elements:
(ii) Electronic configuration:
(iii) The common oxidation state of these elements is . However, highest oxidation state can be .
(iv) Halogens form oxides, hydrogen halides, interhalogen compounds and oxoacids.
(v) Chlorine is obtained by the reaction of with .
(vi) is prepared by heating with concentrated .
(vii) A number of oxoacids of halogens are formed. In the structures of these oxoacids, halogen is the central atom which is bonded in each case with one bond as . In some cases bonds are also found.
5. Group 18 elements (Nobles gases or inert gases)
(i) Elements:
(ii) Electronic configuration: except He which has configuration of .
(iii) All the noble gases except occur in atmosphere.
(iv) Due to complete octet of outermost shell, group elements have less tendency to form compounds. The best characterised compounds are those of xenon with fluorine and oxygen only under certain conditions.
(v) Argon is used to provide inert atmosphere, helium is used in filling balloons for meteorological observations, neon is used in discharge tubes and fluorescent bulbs.
