Suppose the prism of the figure (a) has apex angle and index of refraction (a) What is the smallest angle of incidence for which a ray can enter the left face of the prism and exit the right face? (b) What angle of incidence is required for the ray to exit the prism with an identical angle for its refraction, as it does in the figure (b)?
(a)
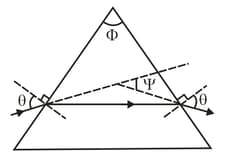
(b)



Important Questions on Electromagnetic Waves
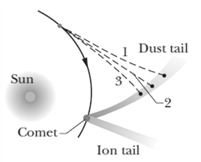
As a comet swings around the sun, ice on the comet's surface vaporizes and releasing trapped dust particles and ions. The ions, because they are electrically charged are forced by the electrically charged solar wind into a straight ion tail that points radially away from the sun (see figure). The (electrically neutral) dust particles are pushed radially outward from the sun by the radiation force on them from sunlight. Assume that, the dust particles are spherical, have density and are totally absorbing. (a) What radius must a particle have in order to follow a straight path like path in the figure? (b) If its radius is larger, does its path curve away from the sun (like path ) or towards the sun (like path )?
Rainbows from square drops. Suppose that, on some surreal world, raindrops had a square cross section and always fell with one face horizontal. Figure shows such a falling drop with a white beam of sunlight incident at at point The part of the light that enters the drop then travels to point where some of it refracts out into the air and the rest reflects. That reflected light then travels to point where again some of the light refracts out into the air and the rest reflects. What is the difference in the angle of the red light and the blue light that emerge at (a) point and (b) point (This angular difference in the light emerging at point would be the rainbow's angular width.)
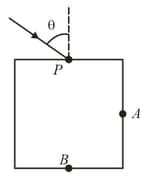
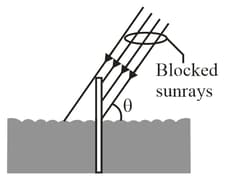
In the figure, a long vertical pole extends from the bottom of a swimming pool to a point above the water. Sunlight is incident at angle . What is the length of the shadow of the pole on the level bottom of the pool?
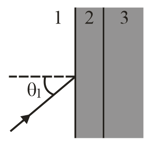
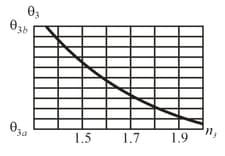
In the figure (a), a beam of light in material is incident on a boundary at an angle Some of the light travels through material and then some of it emerges into material . The two boundaries between the three materials are parallel. The final direction of the beam depends, in part, on the index of refraction of the third material. Figure (b) gives the angle of refraction in that material versus for a range of possible values. The vertical axis scale is set by and (a) What is the index of refraction of a material or is the index impossible to calculate without more information? (b) What is the index of refraction of material or is the index impossible to calculate without more information? (c) If is changed to and the index of refraction of material is what is
(a) (b)
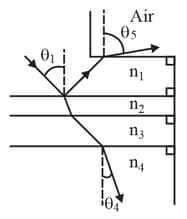
In the figure, the light is incident at an angle on a boundary between two transparent materials. Some of the light travels down through the next three layers of transparent materials, while some of it reflects upward and then escapes into the air. If , and what is the value of (a) in the air and (b) in the bottom material?
An isotropic point source emits light at wavelength at the rate of A light detector is positioned from the source. What is the maximum rate at which the magnetic component of the light changes with time at the detector's location?
