MEDIUM
Earn 100
The Joule Thomson coefficient for an ideal gas is equal to (positive/zero/negative).
50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Chemical Thermodynamics
EASY
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
at
Hence, is:
HARD
,
the amount of heat produced as measured in bomb calorimeter, is at . Assuming ideality the Enthalpy of combustion, , for the reaction will be:
EASY
The heat of reaction for
at constant volume is at . The heat of reaction at constant pressure and same temperature is
EASY
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
(R = 8.314 J/mol K) (ln7.5 = 2.01)
HARD
Tin is obtained from cassiterite by reduction with coke. Use the data given below to determine the minimum temperature (in ) at which the reduction of cassiterite by coke would take place.
Assume that the enthalpies and the entropies are temperature independent.
EASY
MEDIUM
For the reaction
MEDIUM
EASY
For which of the following systems, the difference between and is not significant?
(i) Solids
(ii) Gases
(iii) Mixture of gases and liquids
(iv) Liquids
EASY
HARD
Based on the above thermochemical equations, the value of at for the reaction
will be:
HARD
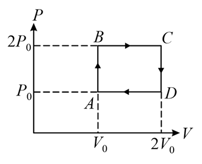
The above diagram represents the thermodynamic cycle of an engine, operating with an ideal mono-atomic gas. The amount of heat, extracted from the source in a single cycle, is:

