EASY
Earn 100
The absorption spectrum and emission spectrum are formed due to the absorption of the energy by electrons.
(a)True
(b)False
50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Use a model to illustrate how photosynthesis transforms light energy into stored chemical energy.
EASY
Life Sciences>From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes>Use a model to illustrate how photosynthesis transforms light energy into stored chemical energy.>Organization for Matter and Energy Flow in Organisms - The process of photosynthesis converts light energy to stored chemical energy by converting carbon dioxide plus water into sugars plus released oxygen.
MEDIUM
Life Sciences>From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes>Use a model to illustrate how photosynthesis transforms light energy into stored chemical energy.>Organization for Matter and Energy Flow in Organisms - The process of photosynthesis converts light energy to stored chemical energy by converting carbon dioxide plus water into sugars plus released oxygen.
MEDIUM
Life Sciences>From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes>Use a model to illustrate how photosynthesis transforms light energy into stored chemical energy.>Organization for Matter and Energy Flow in Organisms - The process of photosynthesis converts light energy to stored chemical energy by converting carbon dioxide plus water into sugars plus released oxygen.
MEDIUM
Life Sciences>From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes>Use a model to illustrate how photosynthesis transforms light energy into stored chemical energy.>Organization for Matter and Energy Flow in Organisms - The process of photosynthesis converts light energy to stored chemical energy by converting carbon dioxide plus water into sugars plus released oxygen.
HARD
Life Sciences>From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes>Use a model to illustrate how photosynthesis transforms light energy into stored chemical energy.>Organization for Matter and Energy Flow in Organisms - The process of photosynthesis converts light energy to stored chemical energy by converting carbon dioxide plus water into sugars plus released oxygen.
HARD
Life Sciences>From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes>Use a model to illustrate how photosynthesis transforms light energy into stored chemical energy.>Organization for Matter and Energy Flow in Organisms - The process of photosynthesis converts light energy to stored chemical energy by converting carbon dioxide plus water into sugars plus released oxygen.
EASY
Life Sciences>From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes>Use a model to illustrate how photosynthesis transforms light energy into stored chemical energy.>Organization for Matter and Energy Flow in Organisms - The process of photosynthesis converts light energy to stored chemical energy by converting carbon dioxide plus water into sugars plus released oxygen.
Which one of the following has the highest wavelength?
EASY
Life Sciences>From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes>Use a model to illustrate how photosynthesis transforms light energy into stored chemical energy.>Organization for Matter and Energy Flow in Organisms - The process of photosynthesis converts light energy to stored chemical energy by converting carbon dioxide plus water into sugars plus released oxygen.
EASY
Life Sciences>From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes>Use a model to illustrate how photosynthesis transforms light energy into stored chemical energy.>Organization for Matter and Energy Flow in Organisms - The process of photosynthesis converts light energy to stored chemical energy by converting carbon dioxide plus water into sugars plus released oxygen.
(A) Hydrogen has one electron in its orbit but it produces several spectral lines.
(R) There are many excited energy levels available.
MEDIUM
Life Sciences>From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes>Use a model to illustrate how photosynthesis transforms light energy into stored chemical energy.>Organization for Matter and Energy Flow in Organisms - The process of photosynthesis converts light energy to stored chemical energy by converting carbon dioxide plus water into sugars plus released oxygen.
EASY
Life Sciences>From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes>Use a model to illustrate how photosynthesis transforms light energy into stored chemical energy.>Organization for Matter and Energy Flow in Organisms - The process of photosynthesis converts light energy to stored chemical energy by converting carbon dioxide plus water into sugars plus released oxygen.
EASY
Life Sciences>From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes>Use a model to illustrate how photosynthesis transforms light energy into stored chemical energy.>Organization for Matter and Energy Flow in Organisms - The process of photosynthesis converts light energy to stored chemical energy by converting carbon dioxide plus water into sugars plus released oxygen.
EASY
Life Sciences>From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes>Use a model to illustrate how photosynthesis transforms light energy into stored chemical energy.>Organization for Matter and Energy Flow in Organisms - The process of photosynthesis converts light energy to stored chemical energy by converting carbon dioxide plus water into sugars plus released oxygen.
EASY
Life Sciences>From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes>Use a model to illustrate how photosynthesis transforms light energy into stored chemical energy.>Organization for Matter and Energy Flow in Organisms - The process of photosynthesis converts light energy to stored chemical energy by converting carbon dioxide plus water into sugars plus released oxygen.
The number of following statement/s which is/are incorrect is ______
A) Line emission spectra are used to study the electronic structure
B) The emission spectra of atoms in the gas phase show a continuous spread of wavelength from red to violet.
C) An absorption spectrum is like the photographic negative of an emission spectrum
D) The element helium was discovered in the sun by spectroscopic method
EASY
Life Sciences>From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes>Use a model to illustrate how photosynthesis transforms light energy into stored chemical energy.>Organization for Matter and Energy Flow in Organisms - The process of photosynthesis converts light energy to stored chemical energy by converting carbon dioxide plus water into sugars plus released oxygen.
MEDIUM
Life Sciences>From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes>Use a model to illustrate how photosynthesis transforms light energy into stored chemical energy.>Organization for Matter and Energy Flow in Organisms - The process of photosynthesis converts light energy to stored chemical energy by converting carbon dioxide plus water into sugars plus released oxygen.
MEDIUM
Life Sciences>From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes>Use a model to illustrate how photosynthesis transforms light energy into stored chemical energy.>Organization for Matter and Energy Flow in Organisms - The process of photosynthesis converts light energy to stored chemical energy by converting carbon dioxide plus water into sugars plus released oxygen.
MEDIUM
Life Sciences>From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes>Use a model to illustrate how photosynthesis transforms light energy into stored chemical energy.>Organization for Matter and Energy Flow in Organisms - The process of photosynthesis converts light energy to stored chemical energy by converting carbon dioxide plus water into sugars plus released oxygen.
MEDIUM
Life Sciences>From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes>Use a model to illustrate how photosynthesis transforms light energy into stored chemical energy.>Organization for Matter and Energy Flow in Organisms - The process of photosynthesis converts light energy to stored chemical energy by converting carbon dioxide plus water into sugars plus released oxygen.
MEDIUM
Life Sciences>From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes>Use a model to illustrate how photosynthesis transforms light energy into stored chemical energy.>Organization for Matter and Energy Flow in Organisms - The process of photosynthesis converts light energy to stored chemical energy by converting carbon dioxide plus water into sugars plus released oxygen.
The graph below represents the absorption spectrum of a major pigment contributing to photosynthesis.
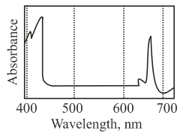
Which one of the following best represents the photosynthetic efficiency of the pigment?

