The boiling points of the halogens are:
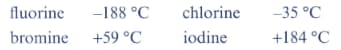
Describe the trend in these boiling points going down Group 17.
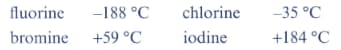

Important Questions on Chemical Bonding
The boiling points of the halogens are:
Explain the trend in these boiling points.
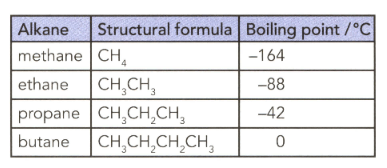
The table lists the formulae and boiling points of some alkanes. Explain the trend in terms of instantaneous dipole-induced dipole forces.
The boiling points of the hydrogen halides are shown in the table.
| Hydrogen halide | HF | HCl | HBr | HI |
| Boiling point / °C | +20 | –85 | –67 | –35 |
Explain the trend in boiling points from to .
The boiling points of the hydrogen halides are shown in the table.
| Hydrogen halide | HF | HCl | HBr | HI |
| Boiling point / °C | +20 | –85 | –67 | –35 |
Explain why the boiling point of HF is so much higher than the boiling point of HCl.
The table lists the boiling points of some Group hydrides.
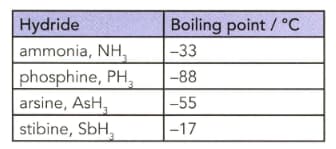
Explain the trend in the boiling points from phosphine to stibine.
The table lists the boiling points of some Group 15 hydrides.
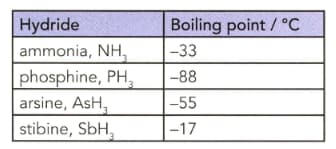
Explain why the boiling point of ammonia does not follow the trend in the boiling points from phosphine to stibine.
Explain the following difference in terms of the type of bonding present.
Aluminium oxide has a melting point of 2980 °C but aluminium chloride changes to a vapour at 178 °C.
