HARD
Earn 100
The change in the magnitude of the volume of an ideal gas when a small additional pressure is applied at a constant temperature, is the same as the change when the temperature is reduced by a small quantity at constant pressure. The initial temperature and pressure of the gas were and respectively. If then value of in is ___________ .
50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Kinetic Theory
MEDIUM
( is universal gas constant and is the acceleration due to gravity)
HARD
A long cylindrical pipe of radius is closed at its upper end and has an airtight piston of negligible mass as shown. When mass is attached to the other end of piston, it moves down by a distance, before coming to equilibrium. Assuming air to be an ideal gas, (see figure) is close to , one atmospheric pressure is ),
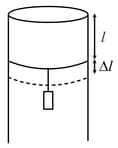
MEDIUM
EASY
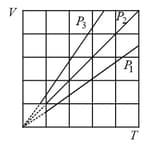
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
EASY
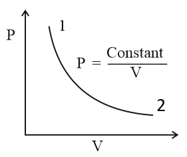
Out of the following which one correctly represents the diagram?
MEDIUM
HARD
EASY
EASY
EASY
HARD
(Atmospheric pressure = of Hg)
MEDIUM
An ideal gas undergoes a circular cycle centred at , as shown in the diagram.
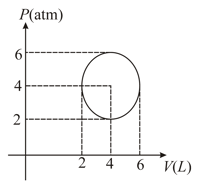
The maximum temperature attained in this process is close to
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
HARD
EASY
EASY

