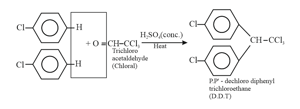
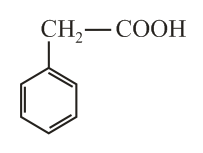
 The compound is
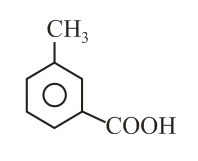
The compound is

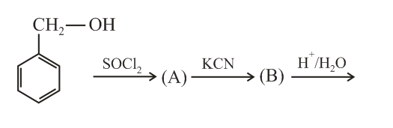
Important Points to Remember in Chapter -1 - Haloalkanes and Haloarenes from Embibe Experts Gamma Question Bank for Engineering Chemistry Solutions
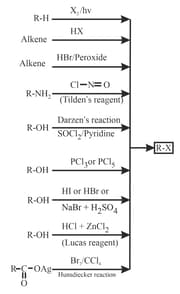
1. Methods of Preparation of Haloalkanes:
2. Physical properties of haloalkanes:
(i) Alkyl halides are colorless with sweet smell or pleasant-smelling oily liquid. However, are gaseous in nature.
(ii) Although carbon-halogen bond is polar in nature, alkyl halides are partially soluble in .
(iii) Alkyl halides are completely soluble in organic solvents.
(iv) Boiling point molecular weight
(v) Chloroform is a pleasant-smelling liquid while iodoform is yellow crystalline solid.
(vi) Chloroform is used as an anesthetic agent.
(vii) Iodoform is more reactive than chloroform due to the large size of iodine atom.
No white ppt of
(viii) Carbon tetrachloride is colorless liquid and used as FIRE EXTINGUISHER under the trade name PYRENE.
(ix) Chloroform is kept in dark-colored bottles to avoid the following oxidation reaction.
(x) Fluorides and chlorides are lighter than water whereas bromides and iodides are heavier than
(xi) is heaviest liquid after .
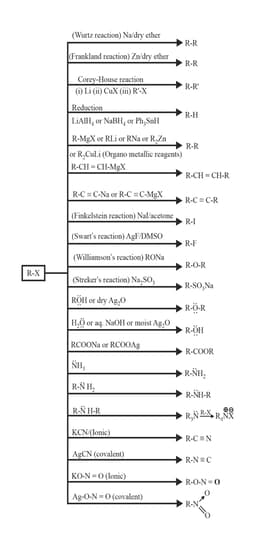
3. Chemical Properties of Haloalkane:
4. Comparison of and reactions:
| A | Kinetics | order | order |
| B | Rate | ||
| C | Stereochemistry | Racemization | Inversion |
| D | Substrate | ||
| E | Nucleophile | Not important | Needs Strong |
| F | Solvent | Faster in protic | Faster in aprotic |
| G | Leaving Group | Needs Good | Needs Good |
| H | Rearrangement | Possible | Not Possible |
5. Comparison of and reactions:
| A | Kinetics | order | order |
| B | Rate | ||
| C | Substrate | ||
| D | Base Strength | Not important | Needs Strong bases |
| E | Solvent | Good ionizing | Polarity not important |
| F | Leaving Group | Needs Good | Needs Good |
| G | Rearrangement | Possible | Not Possible |
6. Identifying and mechanisms:
| Mechanism | Solvent | Temp. | ||
|
Better |
Polar aprotic | Low | ||
| Strong & bulky base | High | |||
| Polar aprotic | Low | |||
| High | ||||
| Solvent | Polar protic | Low | ||
| Solvent | High | |||
| Solvent | Protic | Low | ||
| Solvent | Protic | High |
7. Reactions of Grignard reagent:
Grignard reagent is the most versatile compound as it can be used in the preparation of many different types of compounds.
Grignard reagent is prepared as follows:
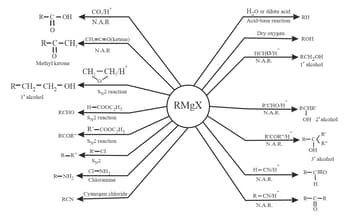
8. Test of Chloroform (Before Anesthetic use):
| Serial Number | Test | Pure | |
| (i) | Litmus paper | ||
| (ii) | No ppt | White ppt | |
| (iii) | No coloration | Yellow color |
9. Preparation methods of haloarenes:
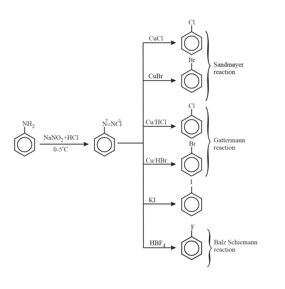
10. Chemical properties of haloarenes:
(i) Addition Elimination reaction:
The presence of electron-withdrawing substituent at ortho and/or para position is a favorable factor for the nucleophilic substitution reaction. More such substituents, the faster the reaction.
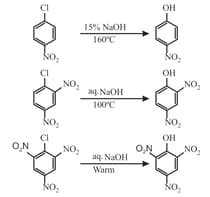
(ii) Mechanism:
(a) reaction takes place by a two steps mechanism.
(b) In the first step nucleophile attacks on the carbon bearing the leaving group.
(c) In the second step the leaving group departs, establishing the aromaticity of the ring.
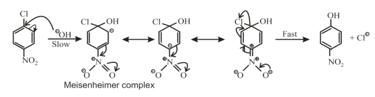
(d) The carbanion is stabilized by electron-withdrawing groups in the positions ortho and para to the halogen atom.
11. Elimination Addition Reaction (Benzyne):
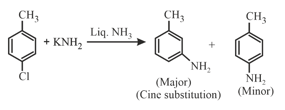
(i) An aromatic halide such as chlorobenzene can undergo nucleophilic substitution in presence of very strong base such as or
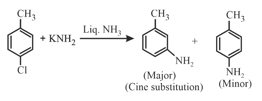
(ii) Substitution at the carbon that was attached to the leaving group is called direct substitution. Substitution at the adjacent carton is called cine substitution.
(iii) Mechanism:
The mechanism of reaction proceeds through benzyne intermediate.
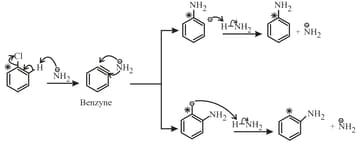
(iv) The substituted halobenzene gives different products through benzyne formation.
(v) The major product formation can be predicted based on the inductive electronic effect of the stability of the intermediate carbanion.
12. Wurtz-Fittig Reaction:

13. Fittig Reaction:

14. Chlorobenzene to :