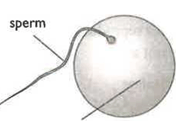
The diagram below shows two gametes: a sperm cell and an egg cell. State one way in which both of these cells differ from other cells of the body.


Important Questions on Reproduction in Humans
The diagram below shows two gametes: a sperm cell and an egg cell. A fertilised egg divides into a ball of cells and becomes attached to the lining of the uterus.
Explain why it is important that this ball of cells soon becomes attached to the lining of the uterus.
The diagram below shows a developing foetus inside its mothers body. Identify the parts labelled A, B and C.
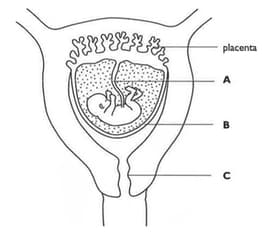
The diagram below shows a developing foetus inside its mothers body. State what causes blood to flow along A.
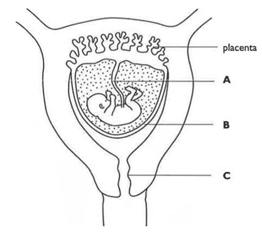
The diagram below shows a developing foetus inside its mothers body. State two substances which pass from the mother to the foetus, and two waste substances which pass from the foetus to the mother.
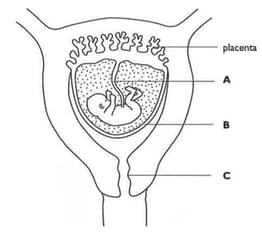
The placenta acts as a barrier keeping the blood of the mother and the foetus separate. Suggest why the blood of the mother is separated from the blood of the foetus.
The placenta acts as a barrier keeping the blood of the mother and the foetus separate. Despite the barrier between the maternal and fetal blood systems, some harmful chemical substances may pass from the mother to the foetus. Suggest one example.
After the baby is born, it's main source of food is milk. Give two advantages of feeding a baby on breast milk rather than using milk prepared from milk powder.
The diagram shows a human sperm.

mitochondrion
