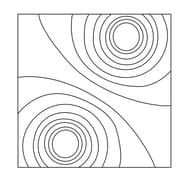
The diagram shows the equipotential lines for two equal and opposite charges. Draw the electric field lines for these two charges.


Important Questions on Fields (HL)
The two long plates are separated by a distance of . The bottom plate is kept at a potential of and the top at . A charge is placed at a point from the bottom plate.
Find the electric potential energy of the charge.
The two long plates are separated by a distance of . The bottom plate is kept at a potential of and the top at . A charge is placed at a point from the bottom plate.
The charge is then moved vertically up to a point from the top plate.
What is the electric potential energy of the charge now
The two long plates are separated by a distance of . The bottom plate is kept at a potential of and the top at . A charge is placed at a point from the bottom plate.
The charge is then moved vertically up to a point from the top plate.
How much work was done on the charge
An electron is shot with a speed equal to from a point where the electric potential is zero towards an immovable negative charge (see the diagram).
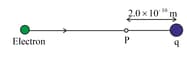
Determine the potential at so that the electron stops momentarily at and turns back. (Use
An electron is shot with a speed equal to from a point where the electric potential is zero towards an immovable negative charge (see the diagram).
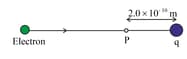
Calculate the magnitude of . (use , )
Two equal and opposite charges are placed at points with coordinates , and , as shown in the diagram.

Find the electric field at the point with coordinates .
Two equal and opposite charges are placed at points with coordinates , and , as shown in the diagram.

Find the electric field at the point with coordinates . for two equal negative charges on the axis.
Two equal and opposite charges are placed at points with coordinates , and , as shown in the diagram.
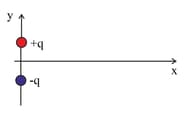
Sketch the graph to show the variation of these fields with the distance .
