HARD
Upper Secondary: IGCSE
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
The diagram shows the forces acting on a cyclist.
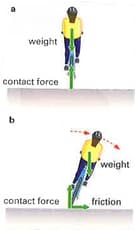
Look at part a of the diagram.
Explain how you can tell that the cyclist shown in part a is in equilibrium.
Now, look at part b of the diagram.
explain how the cyclist is in equillibrium?

explain how the cyclist is in equillibrium?

Important Questions on Turning Effects of Forces
MEDIUM
Upper Secondary: IGCSE
IMPORTANT
The diagram shows the forces acting on a cyclist.

Look at part of the diagram.
Are the forces on the cyclist balanced now How can you tell
MEDIUM
Upper Secondary: IGCSE
IMPORTANT
The diagram shows the forces acting on a cyclist.

Look at part a of the diagram.
Would you describe the cyclist as stable or unstable Explain your answer.
MEDIUM
Upper Secondary: IGCSE
IMPORTANT
Choose the correct word from each pair.
If a force increases, its moment will increase/decrease.
MEDIUM
Upper Secondary: IGCSE
IMPORTANT
Fill the gap with suitable words.
When a body is in equilibrium, the _____(net internal/ net external) force acting on it is zero.
MEDIUM
Upper Secondary: IGCSE
IMPORTANT
Fill the gap with suitable word.
When a body is in equilibrium, the resultant turning effect acting on it is _____.
HARD
Upper Secondary: IGCSE
IMPORTANT
Draw diagrams to show two objects: one with a low centre of mass and a wide base, the other with a high centre of mass and a narrow base. Mark and label the centre of mass each.
HARD
Upper Secondary: IGCSE
IMPORTANT
Label your diagrams stable object and unstable object correctly.
HARD
Upper Secondary: IGCSE
IMPORTANT
A force F acts on a long, straight beam, at a distance x from a pivot.
Draw a diagram to represent this.
