EASY
Earn 100
The energy levels of an hydrogen atom are shown below. The transition corresponding to emission of shortest wavelength is
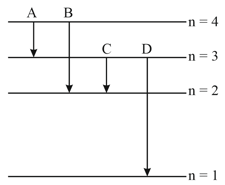

(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
79.03% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Atoms
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
HARD
[Use and are Planck's constant and speed of light, respectively]
MEDIUM
(Given: )
EASY
EASY
HARD
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
HARD
MEDIUM
(for a photon of wavelength , energy )
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
HARD
MEDIUM
HARD
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM

