The figure shown below shows the potential energy of a solid ball that can roll along a axis. The scale on the axis is set by The ball is uniform, rolls smoothly and has a mass of . It is released at headed in the negative direction of the axis with a mechanical energy of . (a) If the ball can reach , what is its speed there and if it cannot, what is its turning point? Suppose instead, it is headed in the positive direction of the axis when it is released at .
(b) If the ball can reach what is its speed there and if it cannot, what is its turning point?
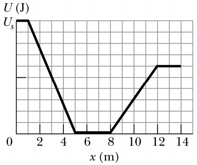
(b) If the ball can reach what is its speed there and if it cannot, what is its turning point?


Important Questions on Rolling, Torque, and Angular Momentum
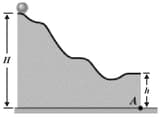
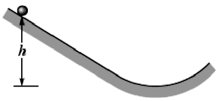
In the figure shown below, a solid ball rolls smoothly from rest (starting at height, ) until it leaves the horizontal section at the end of the track, at height . How far horizontally from point , does the ball hit the floor?
A hollow sphere of radius with rotational inertia about a line through its center of mass rolls without slipping up a surface inclined at to the horizontal. At a certain initial position, the sphere's total kinetic energy is . (a) How much of this initial kinetic energy is rotational? (b) What is the speed of the center of mass of the sphere at the initial position? When the sphere has moved up the incline from its initial position, what are (c) its total kinetic energy and (d) the speed of its center of mass?
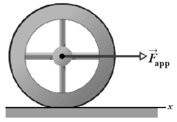
In figure shown below, a constant horizontal force, of magnitude is applied to a wheel of mass and radius . The wheel rolls smoothly on the horizontal surface and the acceleration of its center of mass has magnitude .
(a) In unit-vector notation, what is the frictional force on the wheel?
(b) What is the rotational inertia of the wheel about the rotation axis through its center of mass?
In figure shown below, a solid brass ball of mass will roll smoothly along a loop-the-loop track when released from rest along the straight section. The circular loop has radius, and the ball has radius, .
(a) What is if the ball is on the verge of leaving the track when it reaches the top of the loop? If the ball is released at height, , what is the (b) magnitude and direction of the horizontal force component acting on the ball at point ?
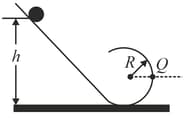
In the figure shown below, a ball of mass and radius rolls smoothly from rest down a ramp and onto a circular loop of radius The initial height of the ball is At the loop bottom, the magnitude of the normal force on the ball is . The ball consists of an outer spherical shell (of a certain uniform density) that is glued to a central sphere (of a different uniform density). The rotational inertia of the ball can be expressed in the general form , but is not as it is for a ball of uniform density. Determine .
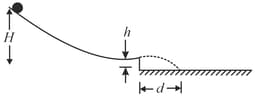
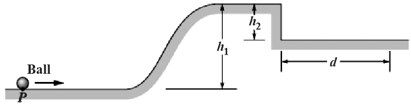
In the figure shown below, a small, solid, uniform ball is to be shot from point , so that it rolls smoothly along a horizontal path, up along a ramp and onto a plateau. Then, it leaves the plateau horizontally to land on a game board, at a horizontal distance from the right edge of the plateau. The vertical heights are , With what speed must the ball be shot at point for it to land at
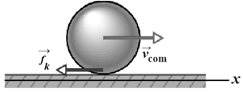
A bowler throws a bowling ball of radius along a lane. The ball in the figure shown below slides on the lane with initial speed and initial angular speed The coefficient of kinetic friction between the ball and the lane is . The kinetic frictional force acting on the ball causes a linear acceleration of the ball while producing a torque that causes an angular acceleration of the ball. When the speed has decreased enough and the angular speed has increased enough, the ball stops sliding and then, rolls smoothly.
(a) What then is in terms of ? During the sliding, what are the ball's (b) linear acceleration and (c) angular acceleration?
(d) How long does the ball slide? (e) How far does the ball slide?
(f) What is the linear speed of the ball when smooth rolling begins?
Consider a non-uniform cylindrical object. In figure shown below, a cylindrical object of mass and radius rolls smoothly from rest down a ramp and onto a horizontal section. From there, it rolls off the ramp and onto the floor, landing a horizontal distance, from the end of the ramp. The initial height of the object is, , the end of the ramp is at height, . The object consists of an outer cylindrical shell (of a certain uniform density) that is glued to a central cylinder (of a different uniform density). The rotational inertia of the object can be expressed in the general form, but is not as it is for a cylinder of uniform density. Determine .