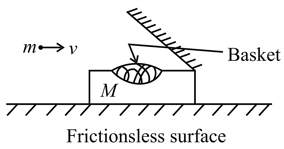
The figure shows a block having a small basket in it and an small inclined plane is rigidly attached to the block. The combined mass (including incline plane) of all these is . Initially they are at rest. Now identical balls each of mass are thrown horizontally with velocity (with respect to ground) which strike the inclined plane and then are collected in the small basket. Assume that in the basket balls come to rest with respect to basket.

Important Questions on Laws of Motion
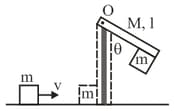
A block of mass slides with velocity on a frictionless horizontal surface and collides with a uniform vertical rod and sticks to it as shown. The rod is pivoted about and swings as a result of the collision making angle before momentarily coming to rest. if the rod has mass and length the value of is approximately
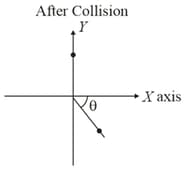
A ball of mass moving with a velocity along -axis, hits another ball of mass which is at rest. After the collision, the first ball comes to rest and the second one disintegrates into two equal pieces. One of the pieces starts moving along -axis at a speed of . The second piece starts moving at a speed of at an angle (degree) with respect to the -axis. The configuration of pieces after the collision is shown in the figure. The value of (in degrees) to the nearest integer is _________.