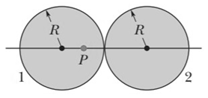
The figure shows a cross-section of two solid spheres with uniformly distributed charge throughout their volumes. Each has a radius Point lies on a line connecting the centers of the spheres, at a radial distance from the center of the sphere . If the net electric field at point is zero, what is the ratio of the total charges?


Important Questions on Gauss' Law
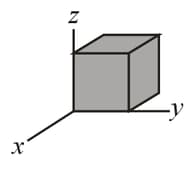
The figure shows a closed Gaussian surface in the shape of a cube of edge length . It lies in a region where the nonuniform electric field is given by with in meters. What is the net charge contained by the cube?
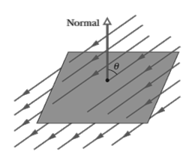
The square surface shown in the figure, measures on each side. It is immersed in a uniform electric field with magnitude and with field lines at an angle of with a normal to the surface, as shown. Take that normal to be directed outward, as though the surface were one face of a box. Calculate the electric flux through the surface. If the angle is reduced by a few degrees, does the flux increases or decreases or remains same.
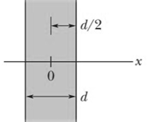
The figure shows a cross-section through a very large nonconducting slab of thickness and uniform volume charge density The origin of an -axis is at the slab's center. What is the magnitude of the slab's electric field at an -coordinate of and
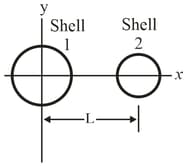
The figure shows two nonconducting spherical shells fixed in place. Shell has uniform surface charge density on its outer surface and radius ; shell has uniform surface charge density on its outer surface and radius the shell centers are separated by In unit-vector notation, what is the net electric field at